Additive Scrambler
Scramble an input stream using a Linear Feedback Shift Register (LFSR).
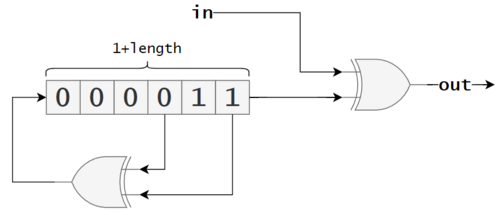
This block scrambles up to 8 bits per byte of the input data stream, starting at the LSB. The scrambler works by XORing the incoming bit stream by the output of the LFSR. Optionally, after bits have been processed, the shift register is reset to the value. This allows processing fixed length vectors of samples.
Alternatively, the LFSR can be reset using a reset tag to scramble variable length vectors. However, it cannot be reset between bytes.
For details on configuring the LFSR, see gr::digital::lfsr.
Parameters
(R): Run-time adjustable
- Mask
- Polynomial mask for LFSR
- Seed
- Initial shift register contents
- Length
- Shift register length
- Count
- Number of bytes after which shift register is reset, 0=never
- Bits per byte
- Number of bits per byte
- Reset tag key
- When a tag with this key is detected, the shift register is reset (when this is set, count is ignored!)
Example Flowgraph
The state diagram for this flowgraph:
This flowgraph can be downloaded from Media:Additive Scrambler.grc.
Generating Gold Codes
Gold Codes can be generated using LFSRs, as explained here.
Output:
This flowgraph can be downloaded from Media:Additive Scrambler Gold Code.grc.
Source Files
- C++ files
- additive_scrambler_impl.cc
- Header files
- additive_scrambler_impl.h
- Public header files
- additive_scrambler.h
- Block definition
- digital_additive_scrambler_bb.block.yml