Writing Binary Files: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "The '''File Sink''' block takes incoming samples and saves them to local storage. ==Block Options for Data Types== By default the '''File Sink''' block uses a 32-bit float format for saving interleaved I and Q:") |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
By default the '''File Sink''' block uses a 32-bit float format for saving interleaved I and Q: | By default the '''File Sink''' block uses a 32-bit float format for saving interleaved I and Q: | ||
[[File:Storing_binary_files_file_sink_complex_floats.png]] | |||
Opening the blocks properties, other formats can be selected from the drop down menu: | |||
[[File:Storing_binary_files_file_sink_types_drop_down.png]] | |||
Another common type is ''float'', represented by '''<span style="color:orange">orange</span>''', which stores real samples as 32-bit floats. | |||
Revision as of 23:02, 5 April 2024
The File Sink block takes incoming samples and saves them to local storage.
Block Options for Data Types
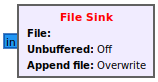
By default the File Sink block uses a 32-bit float format for saving interleaved I and Q:
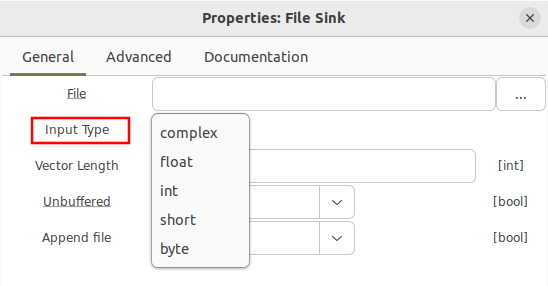
Opening the blocks properties, other formats can be selected from the drop down menu:
Another common type is float, represented by orange, which stores real samples as 32-bit floats.