Vector Source: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Block Docs]] | [[Category:Block Docs]] | ||
This block produces a stream of samples based on an input vector. In C++, this is a std::vector<T>, and in Python, this is either a list or tuple. The data can repeat indefinitely until the flowgraph is terminated by some other event or, the default, run the data once and stop. | |||
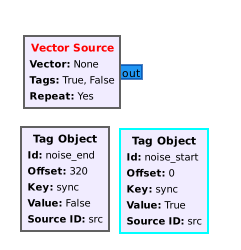
The vector source can also produce stream tags with the data. Pass in a vector of gr::tag_t objects and they will be emitted based on the specified offset of the tag. | The vector source can also produce stream tags with the data. Pass in a vector of gr::tag_t objects and they will be emitted based on the specified offset of the tag. | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
== Example Flowgraph == | == Example Flowgraph == | ||
The following example uses a 0 and a 1 output in a stream to control another block. | |||
[[File:Vector_source_with_tags.png]] | [[File:Vector_source_with_tags.png]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:44, 14 May 2024
This block produces a stream of samples based on an input vector. In C++, this is a std::vector<T>, and in Python, this is either a list or tuple. The data can repeat indefinitely until the flowgraph is terminated by some other event or, the default, run the data once and stop.
The vector source can also produce stream tags with the data. Pass in a vector of gr::tag_t objects and they will be emitted based on the specified offset of the tag.
GNU Radio provides a utility Python module in gr.tag_utils to convert between tags and Python objects: gr.tag_utils.python_to_tag.
Parameters
(R): Run-time adjustable
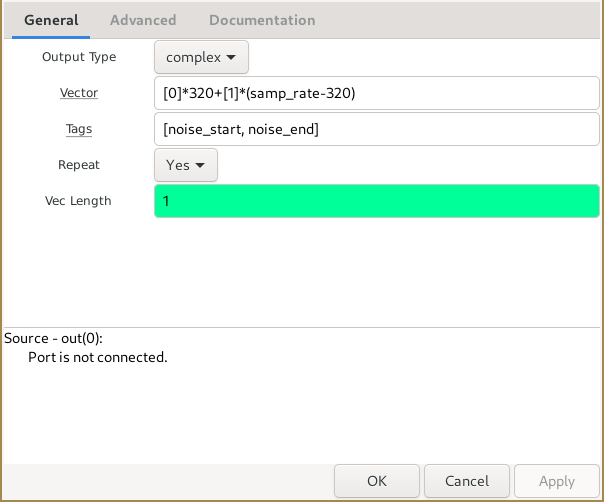
- Output Type
- Output data type of data, possible values are complex, float, int, short, byte
- Default value = complex
- Vector (R)
- Vector to be generated
- Default value = (0, 0, 0)
- Tags (R)
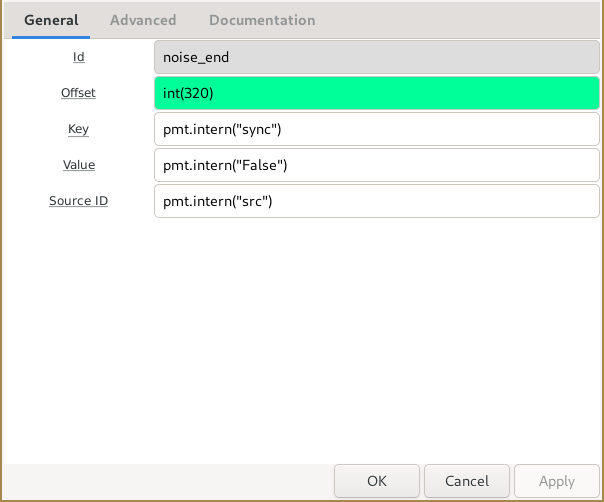
- In Python, we can create tags as Python lists (or tuples) using the list structure [int offset, pmt key, pmt value, pmt srcid]. It is important to define the list/tuple with the values in the correct order and with the correct data type. A python dictionary can also be used using the keys: "offset", "key", "value", and "srcid" with the same data types as for the lists.
- When given a list of tags, the vector source will emit the tags repeatedly by updating the offset relative to the vector stream length. That is, if the vector has 500 items and a tag has an offset of 0, that tag will be placed on item 0, 500, 1000, 1500, etc.
- In gnuradio-companion, make sure to define a "Tag Object" block for each tag. Your input to the "Tags" parameter will be a list of block ids, like seen below in the screenshots. The offset in the vector is decided by the tag object.
- Default value = []
- Repeat
- Whether or not to repeat the vector when it's done
- Vec Length
- Length of the output vector, i.e. if set to 1 then it will output just a normal stream.
Example Flowgraph
The following example uses a 0 and a 1 output in a stream to control another block.
Source Files
- C++ files
- vector_source_impl.cc
- Header files
- vector_source_impl.h
- Public header files
- vector_source.h
- Block definition
- blocks_vector_source_x.block.yml