Stream Mux: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
(Add an example flowgraph) |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
== Example Flowgraph == | == Example Flowgraph == | ||
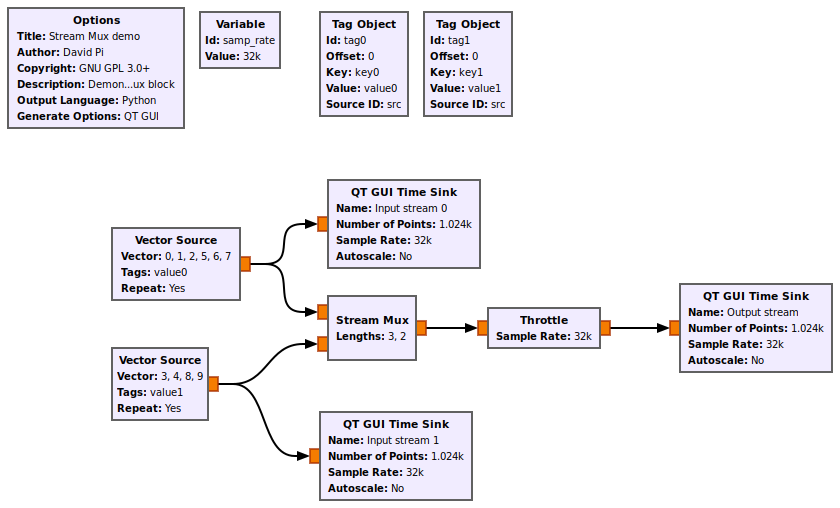
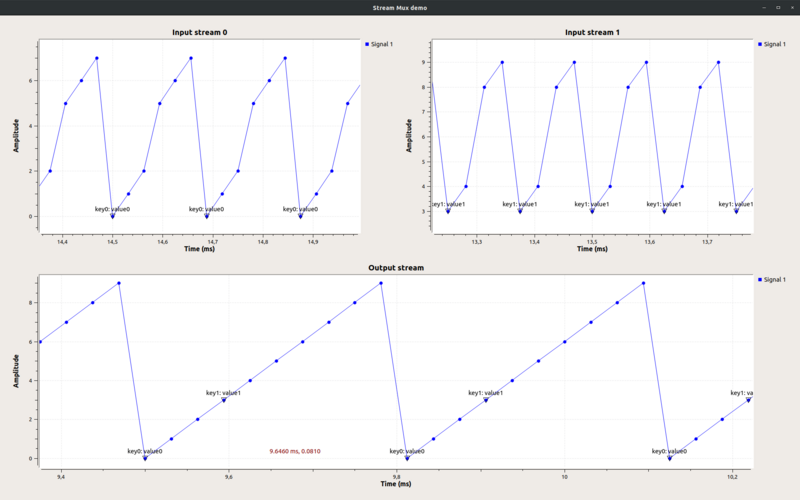
This flowgraph shows the Stream Mux block muxing 2 input streams into an output stream with <tt>lengths = [3, 2]</tt>. The block will take 3 items from the first stream, 2 items from the second stream, and repeat. Notice that tags are preserved. | |||
[[File:stream_mux_demo_flowgraph.png|800x]] | |||
[[File:Stream_mux_demo_exec.png|800px]] | |||
== Source Files == | == Source Files == | ||
Revision as of 11:01, 28 October 2020
Stream muxing block to multiplex many streams into one with a specified format.
Muxes N streams together producing an output stream that contains N0 items from the first stream, N1 items from the second, etc. and repeats:
[N0, N1, N2, ..., Nm, N0, N1, ...]
Parameters
- Lengths
- A vector (list/tuple) specifying the number of items from each stream the mux together. Warning: this requires that at least as many items per stream are available or the system will wait indefinitely for the items.
- Num inputs
- Number of input streams.
Example Flowgraph
This flowgraph shows the Stream Mux block muxing 2 input streams into an output stream with lengths = [3, 2]. The block will take 3 items from the first stream, 2 items from the second stream, and repeat. Notice that tags are preserved.
Source Files
- C++ files
- [1]
- Header files
- [2]
- Public header files
- [3]
- Block definition
- [4]