Stream Demux: Difference between revisions
(Added tags to example) |
m (Fix typo) |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
[[File:stream_demux_demo_flowgraph.png| | [[File:stream_demux_demo_flowgraph.png|800px]] | ||
[[File:Stream_demux_demo_exec.png|800px]] | [[File:Stream_demux_demo_exec.png|800px]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:58, 29 October 2020
Stream demuxing block to demultiplex one stream into N output streams.
Demuxes a stream producing N outputs streams that contains n_0 items in the first stream, n_1 items in the second, etc., and repeats. Tags are propagated. The number of items in each output stream is specified using the lengths parameter like so [n_0, n_1, ..., n_N-1].
Example:
lengths = [2, 3, 4]
input stream = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, ...]
output_stream_0 = [0, 1, 9, 10, ...]
output_stream_1 = [2, 3, 4, 11, ...]
output_stream_2 = [5, 6, 7, 8, ...]
Parameters
- Lengths
- a vector (list/tuple) specifying the number of items to copy to each output stream.
- Num outputs
- Number of output streams.
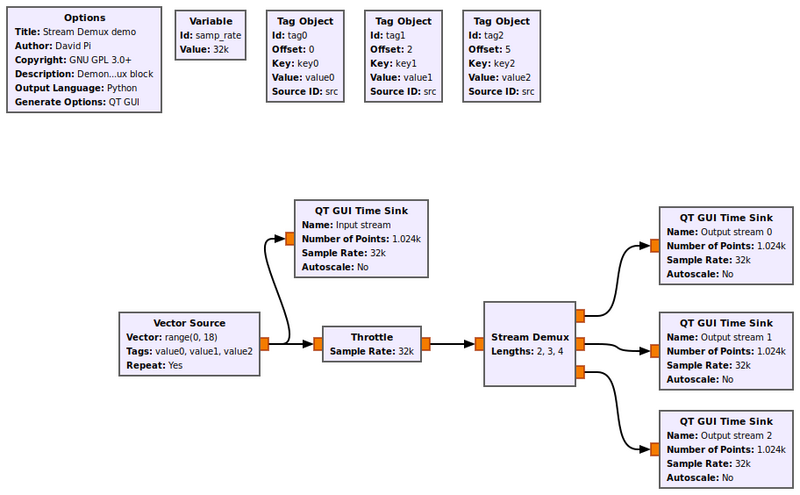
Example Flowgraph
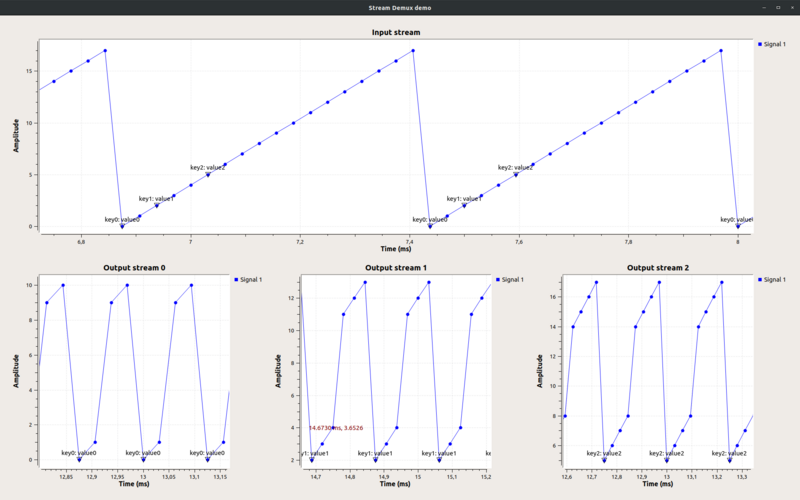
This flowgraph shows the Stream Demux block demuxing an input stream into three output streams with lengths = [2, 3, 4].
The block will put 2 items into the first output stream, 3 items into the second output stream, 4 items into the third output stream, and repeat. Notice that tags are preserved.
Source Files
- C++ files
- [1]
- Header files
- [2]
- Public header files
- [3]
- Block definition
- [4]