Reading Binary Files: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
[[File:Reading_binary_files_all_formats.png]] | [[File:Reading_binary_files_all_formats.png]] | ||
==File Source Block== | |||
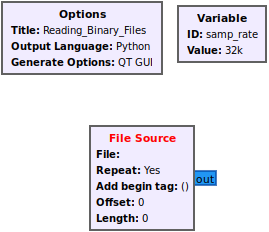
The File Source block reads from a binary file and then sends the samples to the output port. Drag the File Source block into a flowgraph. The block by default uses the complex data type (32-bit floats), represented by the blue output port: | |||
[[File:Reading_binary_files_add_complex_float_file_source.png]] | |||
Revision as of 14:29, 20 April 2024
This tutorial describes how to read binary files using the File Source block along side how to diagnose potential errors.
Please review the Writing Binary Files tutorial before continuing. A series of binary files were created with different formats that will be needed for this tutorial:
File Source Block
The File Source block reads from a binary file and then sends the samples to the output port. Drag the File Source block into a flowgraph. The block by default uses the complex data type (32-bit floats), represented by the blue output port: