Wav File Sink: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Updated parameter description for >= 3.9) |
|||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
== Example Flowgraph == | == Example Flowgraph == | ||
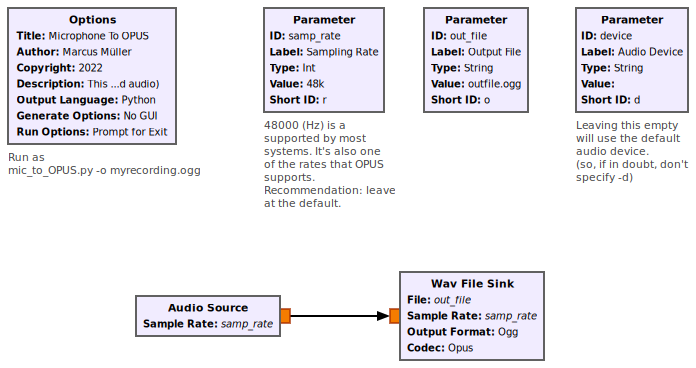
[[File:Mic_to_OPUS.png]] | |||
Non-GUI flow graph. Records a microphone to an OPUS-compressed .ogg file. Very handy. | |||
== Source Files == | == Source Files == | ||
Revision as of 11:00, 26 June 2022
Write stream to a Microsoft PCM (pulse code modulated) (.wav) file (all versions of GNU Radio) and some other file formats that libsndfile supports (GNU Radio 3.9.0.0 and later):
Values must be floats within [-1;1].
Parameters
(R): Run-time adjustable
- File (R)
- Path to the file to write to
- N Channels
- Number of audio channels
- Sample Rate
- Sample rate of the recording
- Output Format (GNU Radio 3.9 and later)
- choice of possible container/audio formats:
- WAV (old-school windows RIFF sound files)
- FLAC (lossless audio codec – probably a good choice for storage of actual audio data)
- Ogg file (Container for lossy compression – allows for choice of vorbis, or OPUS, as audio codec. Prefer OPUS. Very good quality.)
- 64-bit WAV (RF64, used in broadcasting standards, to support massive multichannel files, and files > 4 GB)
- Bits per Samples (only WAV, FLAC, 64-bit WAV)
- Bit-depth of the recording.
- Rule of thumb: you don't need more than 2 + (audio SNR)·2 bits of integer bitdepth to keep quantization noise below signal noise.
- "Float" always suffices, but is wasteful on size, if you're using "Double" without having written down a calculation why, you're doing it wrong
Example Flowgraph
Non-GUI flow graph. Records a microphone to an OPUS-compressed .ogg file. Very handy.
Source Files
- C++ files
- TODO
- Header files
- TODO
- Public header files
- TODO
- Block definition
- TODO