Constellation Object: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
[[File:constellation_soft_decoder_ex.png|800px]] | [[File:constellation_soft_decoder_ex.png|800px]] | ||
== Source Files == | |||
; C++ files | |||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/0fa281fd7369348dbdeadcecfebb20b73082e93e/gr-digital/lib/constellation.cc see middle of this page] | |||
; Header files | |||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio TODO] | |||
; Public header files | |||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/0fa281fd7369348dbdeadcecfebb20b73082e93e/gr-digital/include/gnuradio/digital/constellation.h Here] | |||
; Block definition | |||
: TODO | |||
Revision as of 04:11, 3 August 2019
GNU Radio supports the creation and use of Constellation objects for many of its digital communications needs. We define these constellations with a set of constellation points in complex space and the symbol mappings to those points. For a constellation that has 4 symbols, it then has log2(4) = 2 bits/symbol. We define this constellation with a list of Constellation Points and Symbol Map. For example, 16QAM would have:
Constellation Points = [(-3-3j), (-1-3j), (1-3j), (3-3j), (-3-1j), (-1-1j), (1-1j), (3-1j), (-3+1j), (-1+1j), (1+1j), (3+1j), (-3+3j), (-1+3j), (1+3j), (3+3j)] Symbol Map = [0, 4, 12, 8, 1, 5, 13, 9, 3, 7, 15, 11, 2, 6, 14, 10]
The mapping is a 1-to-1 for the items in both lists. The symbols are referred to as the 'pre_diff_code' since this is the mapping before the application of differential modulation, if used.
See [1] for more info.
Parameters
- Constellation Type
- Type of modulation scheme. Choose Variable Constellation for more control.
- Soft Decisions Precision
- Specifies how accurate the look up table (LUT) is to a given number of bits.
- Soft Decisions LUT
- Vector of floating point tuples that acts as the look up table (LUT). Can be set to 'auto' for GNU Radio to populate it.
- Symbol Map
- (Available when using Variable Constellation) Manually specify the symbol map, in list form.
- Constellation Points
- (Available when using Variable Constellation) Manually specify the constellation points, using a list of complex numbers.
- Rotational Symmetry
- (Available when using Variable Constellation) The number of rotations per 360 degrees that the constellation is symmetric, which is 4 for the common constellations.
- Dimensionality
- (Available when using Variable Constellation) The number of dimensions, typically set to 1.
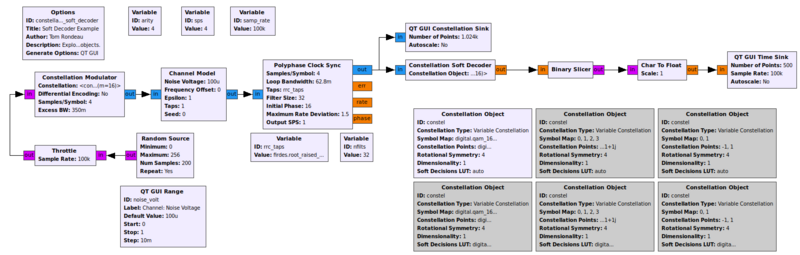
Example Flowgraph
This flowgraph generates symbols using a chosen modulation scheme, runs the signal through a channel model, and then simulates a receiver by synchronizing to the signal and performing soft decoding.
Source Files
- C++ files
- see middle of this page
- Header files
- TODO
- Public header files
- Here
- Block definition
- TODO