Talk:ModuleNotFoundError: Difference between revisions
IndianaM1ke (talk | contribs) (Change wording in intro) |
IndianaM1ke (talk | contribs) (reword into again for more OS clarify) |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
If you get this error message, try | If you get this error message and you're running Linux, try the instructions on this page to see if any of them fix the issue. For issues and settings for OSX, see the [https://wiki.gnuradio.org/index.php/MacInstall#Typical_Errors_and_Warnings MacInstall guide]. | ||
== A. | == A. Determine the GNU Radio install prefix == | ||
If you don't know or remember your installation prefix, perform the following step: | If you don't know or remember your installation prefix, perform the following step: | ||
| Line 22: | Line 18: | ||
then use that prefix in place of <code>{PREFIX}</code> in the following commands. | then use that prefix in place of <code>{PREFIX}</code> in the following commands. | ||
== | == B. Finding the Python library == | ||
Using your file manager, look in <code>{PREFIX}/lib</code> for a directory to match your Python version. For example, <code>python2.7</code> or <code>python3.7</code>; note the combination of <code>python</code> and the version as <code>{major}.{minor}</code>, which is used by all Python installs by default. Use that directory name in place of <code>{PY-VERSION}</code> in the following commands. | Using your file manager, look in <code>{PREFIX}/lib</code> for a directory to match your Python version. For example, <code>python2.7</code> or <code>python3.7</code>; note the combination of <code>python</code> and the version as <code>{major}.{minor}</code>, which is used by all Python installs by default. Use that directory name in place of <code>{PY-VERSION}</code> in the following commands. | ||
== | == C. Setting PYTHONPATH == | ||
- For almost all Debian / Ubuntu (and derivative) systems, and most other 32-bit Unix/Linux systems, use: | - For almost all Debian / Ubuntu (and derivative) systems, and most other 32-bit Unix/Linux systems, use: | ||
| Line 38: | Line 34: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
== | == D. Setting LD_LIBRARY_PATH == | ||
- For almost all Debian / Ubuntu (and derivative) systems, and most other 32-bit Unix/Linux systems, use: | - For almost all Debian / Ubuntu (and derivative) systems, and most other 32-bit Unix/Linux systems, use: | ||
| Line 50: | Line 46: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
== | == E. Store the commands in a Bash start-up file == | ||
Once you have determined the correct two export commands to use, open your text editor and put them in your <code>~/.profile</code> or <code>~/.bash_aliases</code> or <code>~/.bashrc</code> file and restart your terminal.<br> | Once you have determined the correct two export commands to use, open your text editor and put them in your <code>~/.profile</code> or <code>~/.bash_aliases</code> or <code>~/.bashrc</code> file and restart your terminal.<br> | ||
Revision as of 14:28, 30 January 2020
When you start gnuradio-companion or execute grcc, if the system isn't configured properly for GRC to find the GNU Radio Python scripts and/or libraries, then you will see an error message similar to this one:
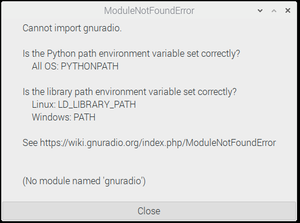
If you get this error message and you're running Linux, try the instructions on this page to see if any of them fix the issue. For issues and settings for OSX, see the MacInstall guide.
A. Determine the GNU Radio install prefix
If you don't know or remember your installation prefix, perform the following step:
- on a terminal screen, enter
gnuradio-config-info --prefix
then use that prefix in place of {PREFIX} in the following commands.
B. Finding the Python library
Using your file manager, look in {PREFIX}/lib for a directory to match your Python version. For example, python2.7 or python3.7; note the combination of python and the version as {major}.{minor}, which is used by all Python installs by default. Use that directory name in place of {PY-VERSION} in the following commands.
C. Setting PYTHONPATH
- For almost all Debian / Ubuntu (and derivative) systems, and most other 32-bit Unix/Linux systems, use:
export PYTHONPATH={PREFIX}/lib/{PY-VERSION}/dist-packages:{PREFIX}/lib/{PY-VERSION}/site-packages:$PYTHONPATH
- For other 64-bit systems, use:
export PYTHONPATH={PREFIX}/lib64/{PY-VERSION}/site-packages:$PYTHONPATH
D. Setting LD_LIBRARY_PATH
- For almost all Debian / Ubuntu (and derivative) systems, and most other 32-bit Unix/Linux systems, use:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH={PREFIX}/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
- For other 64-bit systems, use:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH={PREFIX}/lib64:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
E. Store the commands in a Bash start-up file
Once you have determined the correct two export commands to use, open your text editor and put them in your ~/.profile or ~/.bash_aliases or ~/.bashrc file and restart your terminal.