Add System Time: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Explain UNIX time (I know, I know.)) |
(Caveat: PC clock != SDR clock) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
This block adds a user specified key to PDU dict containing the boost system time in seconds since unix epoch (00:00:00 UTC on 1 January 1970). | This block adds a user specified key to PDU dict containing the boost system time in seconds since unix epoch (00:00:00 UTC on 1 January 1970). | ||
== Caveats == | |||
Note that the computer's clock that this time comes from is in general '''not''' synchronized to the sampling clock of the SDR you might be using. That means, for example, that the timestamps for two PDUs that are (logically) N samples apart do not necessarily differ by N/(sample rate). The notion of different devices with different clocks of time is not deterministic! | |||
== Parameters == | == Parameters == | ||
Latest revision as of 15:50, 13 December 2021
Adds system time to a PDU's metadata.
Added in 3.10
This block adds a user specified key to PDU dict containing the boost system time in seconds since unix epoch (00:00:00 UTC on 1 January 1970).
Caveats
Note that the computer's clock that this time comes from is in general not synchronized to the sampling clock of the SDR you might be using. That means, for example, that the timestamps for two PDUs that are (logically) N samples apart do not necessarily differ by N/(sample rate). The notion of different devices with different clocks of time is not deterministic!
Parameters
(R): Run-time adjustable
- Key
- default: "system_time"
Messages
Inputs
- pdu
- input message
Outputs
- pdu
- output message
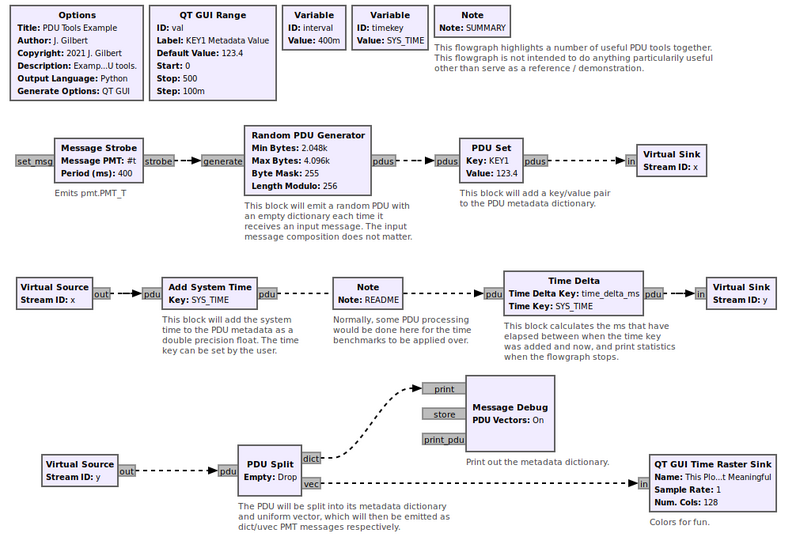
Example Flowgraph
This flowgraph can be found at [1]
Source Files
- C++ files
- TODO
- Header files
- TODO
- Public header files
- TODO
- Block definition
- [2]