Frequency Shifting
This tutorial describes how to perform frequency shifting, causing the frequency of a signal to change.
Frequency Shifting
Frequency shifting is the process of changing the position of a signal within the frequency domain. Equivalently, it can be stated that frequency shifting is the process of changing the center frequency of a signal. Frequency shifted can be implemented many different ways, although this tutorial will focus on the simple method of multiplication by a complex sinusoid.
Multiplying a signal by a complex sinusoid with frequency f Hz will translate or shift the center frequency of the signal by f Hz. For example, to frequency shift a signal by 1 MHz a complex signal must be generated with frequency 1 MHz, and then multiplied against the desired signal in order to frequency shift it.
Build Example Signal
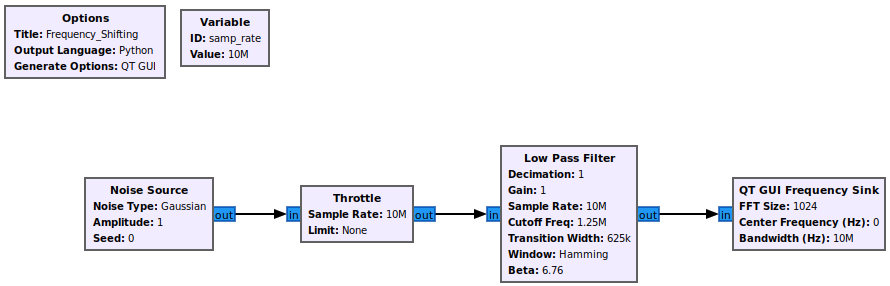
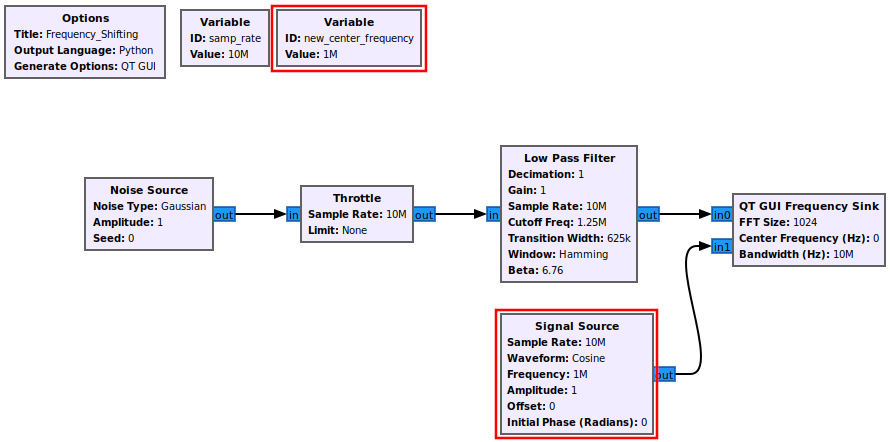
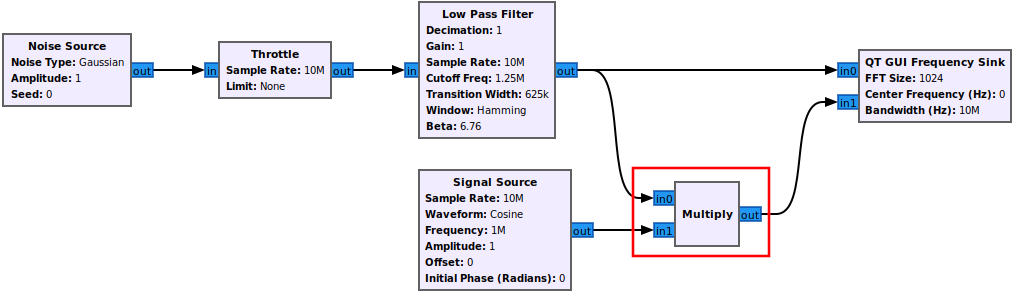
First an example signal needs to be built. A simple signal of filtered noise is created. Drag in the following blocks and connect them:
- Noise Source
- Throttle
- Low Pass Filter
- QT GUI Frequency Sink
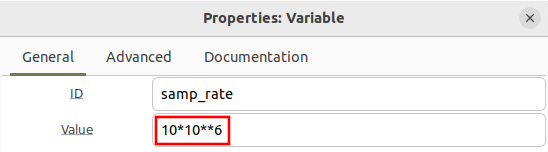
The flowgraph is an offline simulation to the choice of sampling rate is somewhat arbitrary, but a sample rate of 10 MHz is chosen to realistic number.
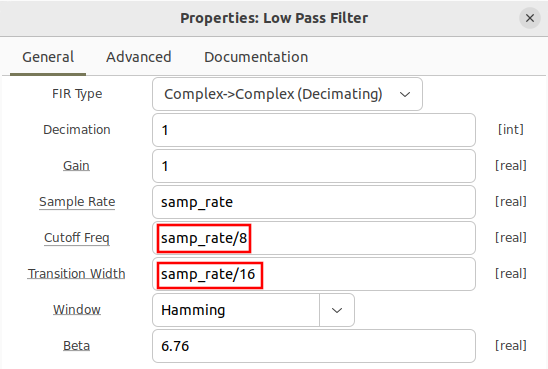
The low-pass filter properties are updated to define the cutoff frequency and transition width:
- Cutoff Freq: samp_rate/8
- Transition Width: samp_rate/16
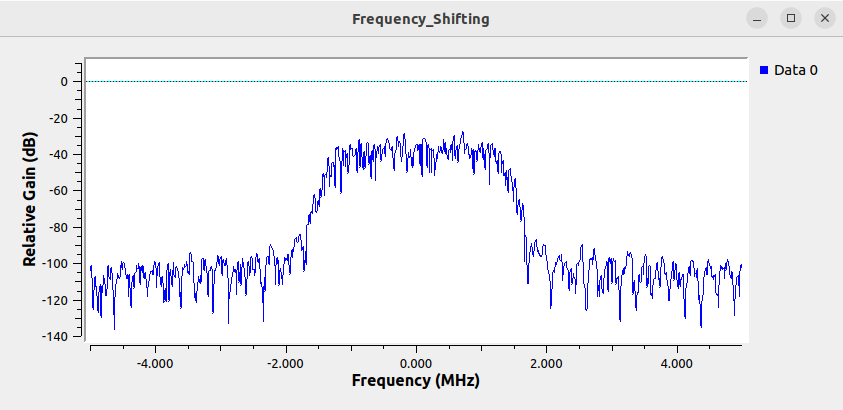
Running the flowgraph then displays a simulated signal:
The signal has not been shifted yet and therefore has a center frequency of 0 Hz.
Create Complex Sinusoid
A complex sinusoid is added to the flowgraph which will be used later to perform the frequency shifting. Add the following blocks and connect them to the flowgraph:
- Variable
- Signal Source
The flowgraph is an offline simulation to the choice of sampling rate is somewhat arbitrary, but a sample rate of 10 MHz is chosen to be a realistic number.
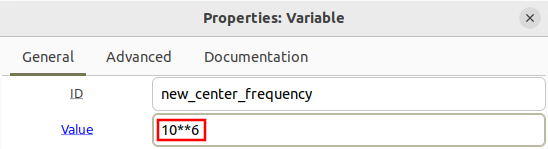
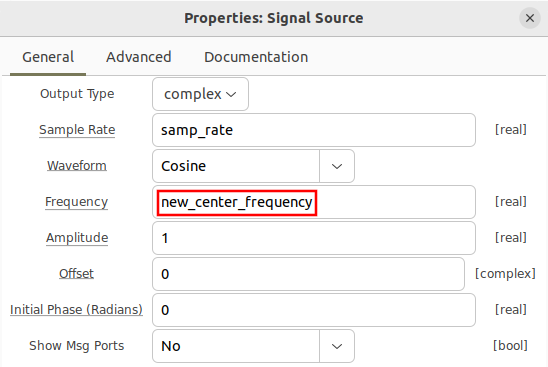
The variable new_center_frequency is then used for the frequency in the signal source block:
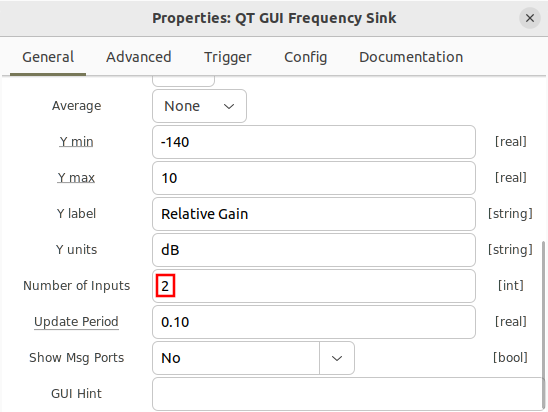
Increase the number of ports on the QT GUI Frequency Sink:
Now run the flowgraph:
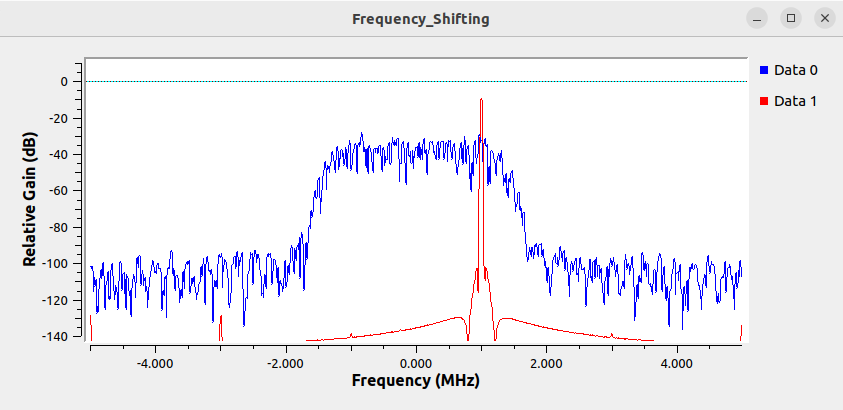
You can now see the new complex sinusoid that has been created and displayed in red:
The frequency shifting process will apply the blue signal against the red complex sinusoid, centering it at 1 MHz.
Perform Frequency Shifting
Add the Multiply block into the flowgraph and connect it such that it accepts the outputs from Low Pass Filter and Signal Source:
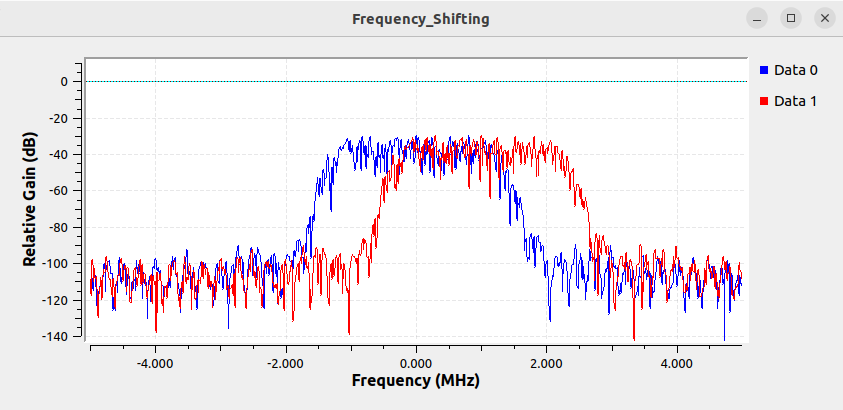
The multiply block now performs the frequency shifting, moving the center frequency of the signal up to 1 MHz. Running the flowgraph shows the input signal centered at 0 Hz and the frequency shifted version at 1 MHz:
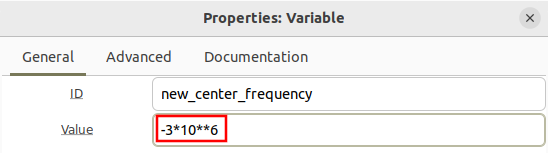
The frequency shifted value can be positive or negative. Update the new_center_frequency variable to be -3 MHz:
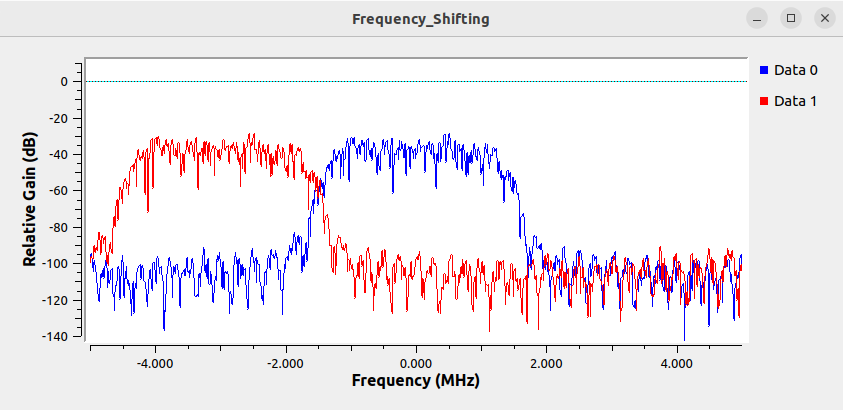
Running the flowgraph now shows the signal centered at -3 MHz:
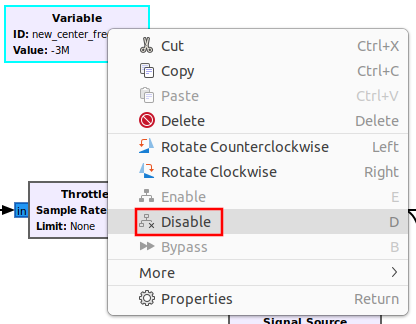
A QT GUI Range block can be used to change the center frequency in real time. Right click on the new_center_frequency and select Disable:
The block will now be grayed out.
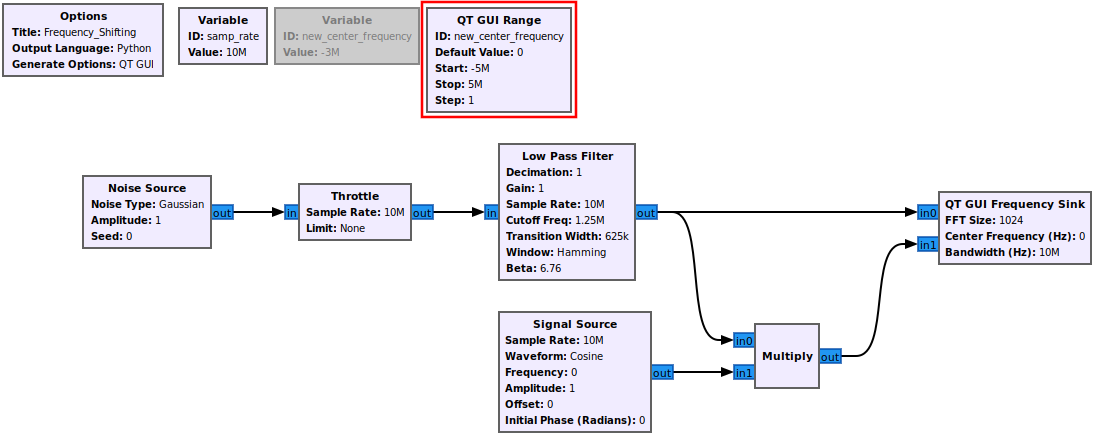
Add a QT GUI Range block to the flowgraph:
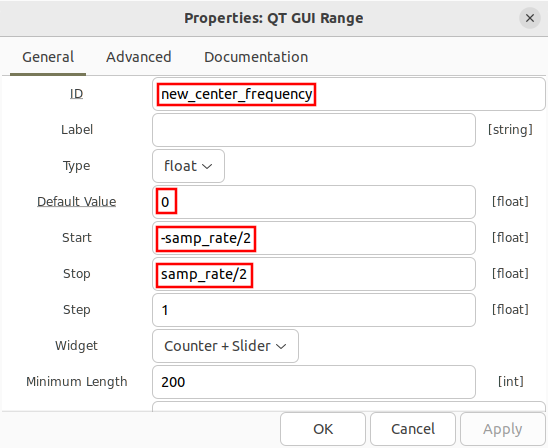
Open the QT GUI Range block and update the following properties:
- ID: new_center_frequency
- Default Value: 0
- Start: -samp_rate/2
- Stop: samp_rate/2