RFNoC Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) Block
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
The RFNoC FFT block performs fast Fourier Transform on input signals, converting them from time-domain to frequency-domain or reverse. It leverages FPGA acceleration for high-throughput and real-time processing.
Parameters
(R): Run-time adjustable
- FFT Block Version
- Number of Channels
- default: 1
- This specifies the number of channels / streams to be used with the block.
- Block Args
- default: ""
- Viable properties can be found at RFNoC FFT control.
- Device Select / Instance Select
- Default: -1 / Default: -1
- These properties specify the device and instance to be used. It is best practice to always explicitly specify both. This is crucial because many USRP setups involve multiple instances of different blocks, and GNU Radio tends to select the first device or instance it finds, which may not be the most suitable choice. Explicit specification helps to prevent errors and ensures the correct setup is used.
- - Use uhd_usrp_probe to determine the correct device and instance numbers.
- - Always specify the device and instance explicitly to avoid automatic mismatches by GNU Radio.
- Even with a single device with multiple instances:
- - 0/Radio#0 → Device 0, Instance 0
- - 0/Radio#1 → Device 0, Instance 1
- Specification with multiple devices:
- - 0/Radio#1 → Device 0, Instance 1
- - 1/Radio#1 → Device 1, Instance 1
- By consistently specifying the device and instance, you ensure that the most appropriate settings are applied and avoid potential issues caused by automatic selection.
- FFT Length
- default: 256
- The FFT length determines the number of points to be used in the FFT computation. A higher value results in higher frequency resolution but also increases computational load.
- FFT Direction
- default: 'FORWARD'
- options: ['Reverse', 'Forward']
- 'Forward': Computes the FFT in the forward direction, transforming the time-domain signal into the frequency domain.
- 'Reverse': Computes the inverse FFT, transforming a frequency-domain signal back into the time domain.
- FFT Magnitude Mode
- default: 'COMPLEX'
- options: ['Complex', 'Magnitude', 'Mag Squared']
- Defines the mode for computing the FFT magnitude.
- 'Complex': Outputs the complex FFT result without any magnitude conversion.
- 'Magnitude': Computes and outputs the magnitude of the FFT result.
- 'Mag Squared': Outputs the squared magnitude of the FFT result.
- FFT Shift Configuration
- default: 'NORMAL'
- options: ['Normal', 'Reverse', 'Natural']
- Specifies how the FFT output is configured with respect to frequency spectrum shifting.
- The input order that this module receives is a parameter that must be chosen at compile time. The following input orders are supported:
- 'Natural': Positive frequencies are input first, starting with 0 Hz, followed by negative frequencies. Frequencies are input in ascending order.
- 'Bit Reverse': Like Natural, but the bits of the indices are in reverse order. For example, for a size 16 FFT, bin 0000 is input first, followed by bin 1000, 0100, 1100, 0010, etc.
- The output order can be chosen at run time. The following output orders are supported:
- 'Normal': Negative frequencies first, then positive frequencies. 0 Hz is in the center. Frequencies are output in ascending order.
- 'Reverse': Reverse order of NORMAL. Positive frequencies first, then negative frequencies. 0 Hz in the center. Frequencies are output in descending order
- 'Natural': Positive frequencies are first, starting with 0 Hz, followed by negative frequencies. Frequencies are output in ascending order.
- 'Bit Reverse': Like natural, but the bits of the indices are in reverse order. For example, for a size 16 FFT, bin 0000 is output first, followed by bin 1000, 0100, 1100, 0010, etc.
- Choose FFT Scaling
- default: 'Scaling Schedule'
- options: ['Scaling Schedule', 'Scaling Factor']
- This parameter allows the user to choose between two methods of scaling the FFT output described below.
- FFT Scaling Schedule
- default: 170
- Ensures numerical accuracy and maintains the dynamic range of the FFT output, preventing overflow or underflow issues. Users can adjust it to meet specific application needs.
- FFT Scaling Factor
- default : 1.0
- This is a convenience function which can be used instead of FFT Scaling Schedule. Based on the given factor, it automatically sets the scaling mask by evenly distributing the scaling across the active FFT stages.
- Examples:
- - factor = 1.0 -> no scaling
- - factor = 0.5 (1/2)
- -> scale by 2 in the first FFT stage
- - factor = 0.0625 (1/16)
- -> scale by 4 in both the first and the second FFT stage
- - factor = 0.03125 (1/32) ->
- -> scale by 4 in both the first and the second FFT stage and by 2 in the third FFT stage
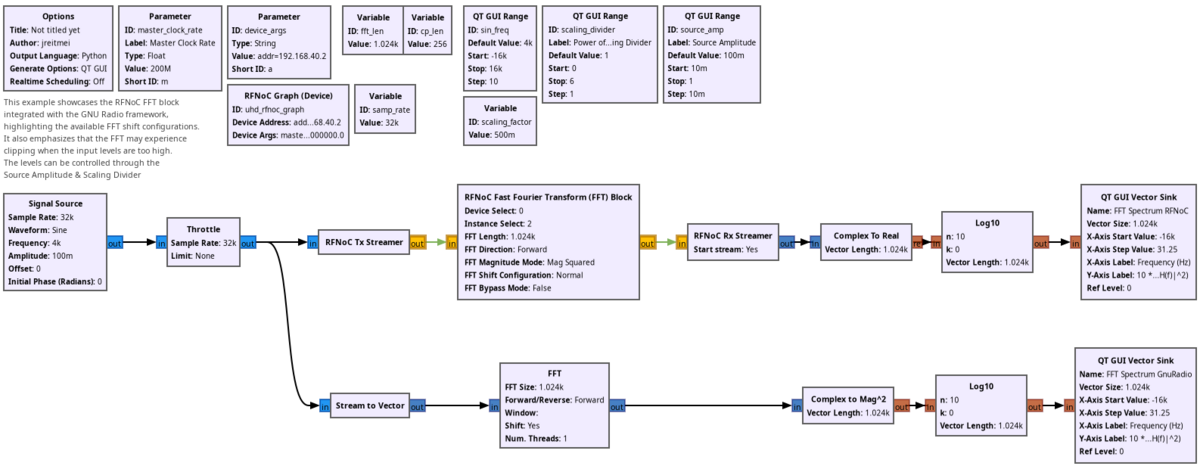
Example Flowgraph
You can find this example at rfnoc_fft_forward.grc
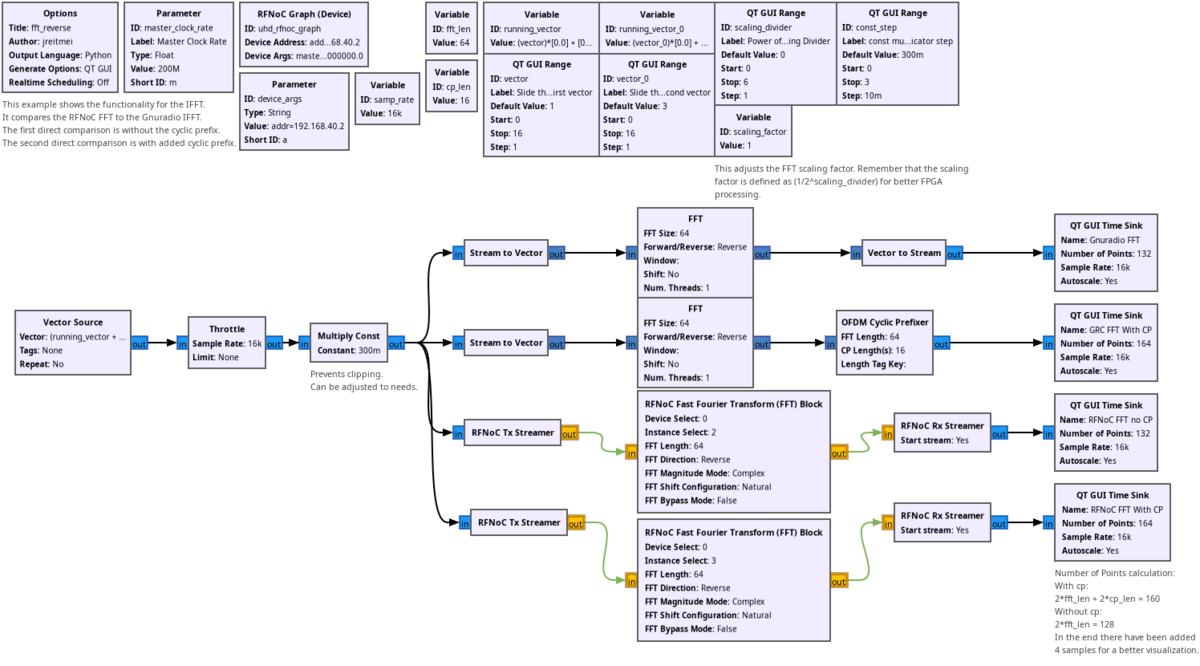
You can find this example at rfnoc_fft_reverse.grc
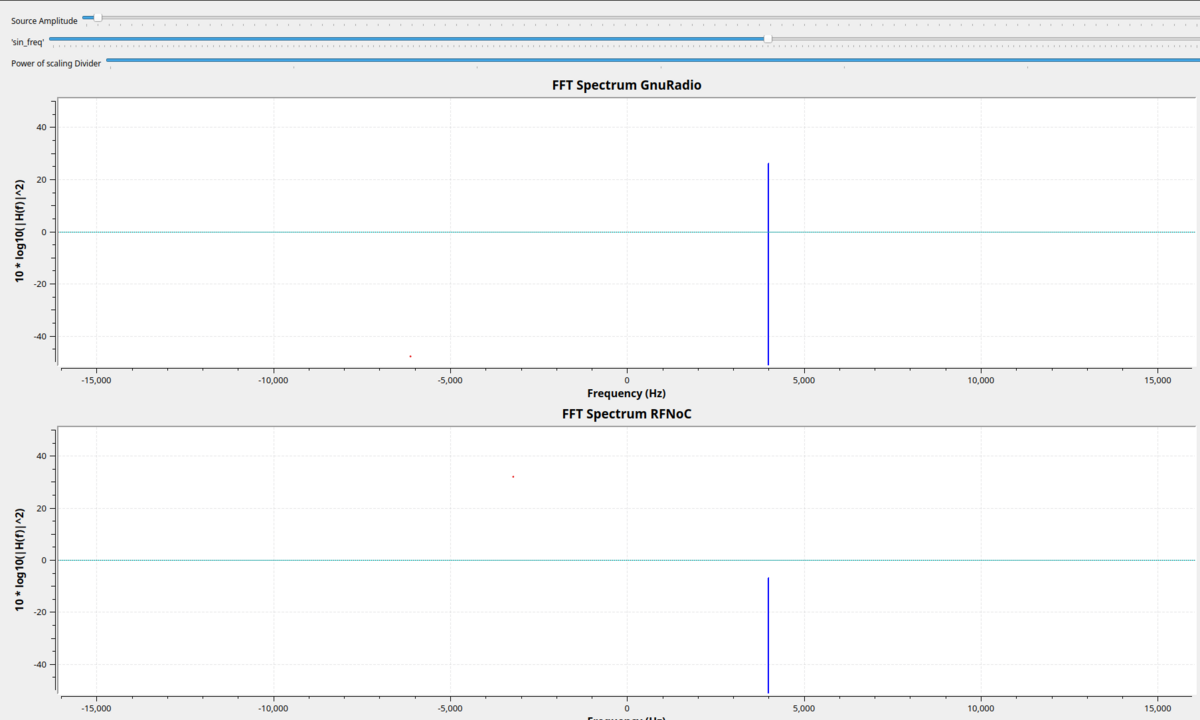
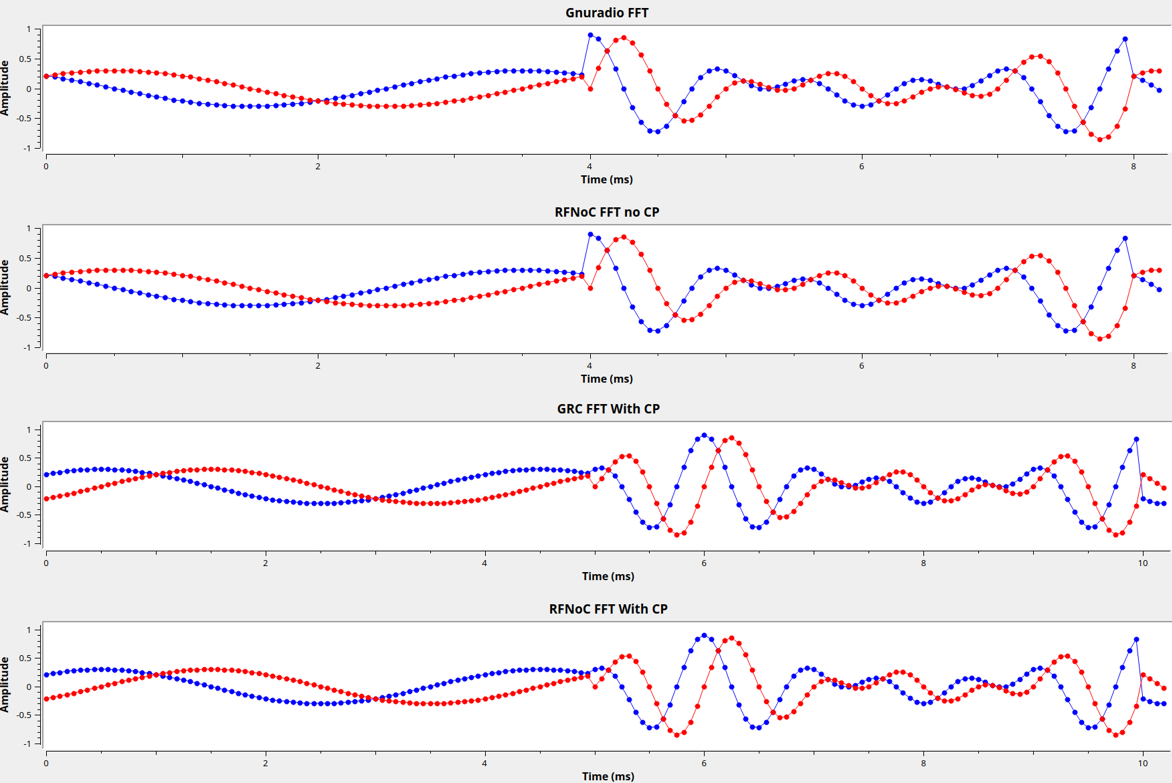
Example Output
Source Files
- C++ files
- rfnoc_fft_impl.cc
- Header files
- rfnoc_fft_impl.h
- Public header files
- rfnoc_fft.h
- Block definition
- uhd_rfnoc_fft.block.yml