Signal Data Types
This section describes the data types which can be used to represent signals. The starting flowgraph from Your First Flowgraph is used in this section.
Data Types
Every input and output port on a block will have a data type associated with it. The data type is identified by the color of the input and output port. The GNU Radio data types can be found by opening GNU Radio Companion (GRC) and clicking Help, Types:
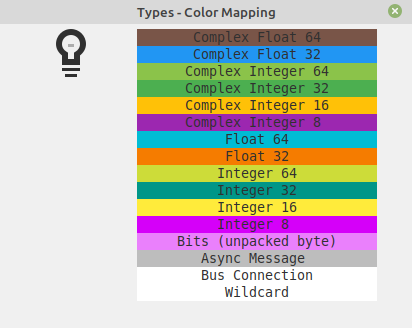
A window displays the data types and their associated colors:
The most common data types in GNU Radio blocks are Complex Float 32 in blue and Float 32 in orange.
Complex Data Type
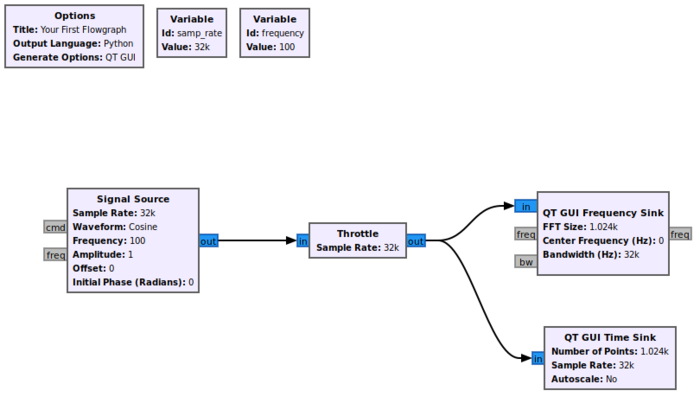
The following flowgraph uses the Complex Float 32 data type, which uses a 32-bit float to represent the real and imaginary portions of a complex sample.
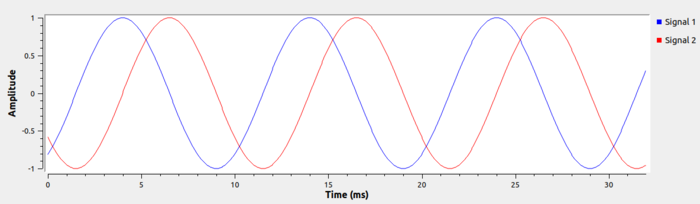
Running the flowgraph shows the complex signal plotted in the time domain, where Signal 1 is the real component and Signal 2 is the imaginary component of the complex signal:
Each complex sample is therefore 64 bits: a 32-bit float for the real component, and a 32-bit float for the imaginary component.