Frequency Mod: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m (→Parameters) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
More specifically, takes a real, baseband signal (x_m[n]) and output a frequency modulated signal (y[n]) according to: | More specifically, takes a real, baseband signal (x_m[n]) and output a frequency modulated signal (y[n]) according to: | ||
[[File:freq-mod-1.png| | [[File:freq-mod-1.png|150px]] | ||
Where x[n] is the input sample at time n and is the frequency deviation. Common values for | Where x[n] is the input sample at time n and <math>f_{\Delta}</math> is the frequency deviation. Common values for <math>f_{\Delta}</math> are 5 kHz for narrowband FM channels such as for voice systems and 75 kHz for wideband FM, like audio broadcast FM stations. In this block, the input argument is sensitivity, not the frequency deviation. The sensitivity specifies how much the phase changes based on the new input sample. Given a maximum deviation <math>f_{\Delta}</math>, and sample rate <math>f_s</math>, the sensitivity is defined as: | ||
[[File:freq-mod-2.png| | [[File:freq-mod-2.png|50px]] | ||
== Parameters == | == Parameters == | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
; Sensitivity (''R'') | ; Sensitivity (''R'') | ||
: | : Sensitivity = (2 * math.pi * deviation) / sample_rate | ||
: where 'deviation' is the change of the frequency when the input is at the values of -1 or +1. If the input is outside [-1, +1], it can deviate more. | |||
== Example Flowgraph == | == Example Flowgraph == | ||
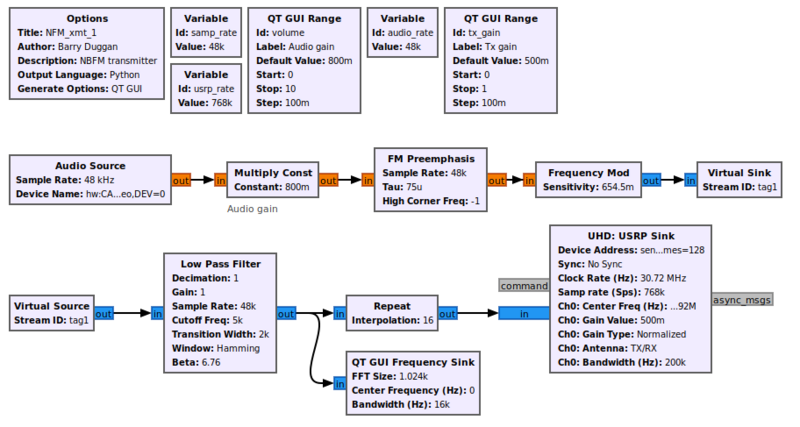
[[File:NFM_xmt_2_fg.png|800px]] | |||
== Source Files == | == Source Files == | ||
; C++ files | ; C++ files | ||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio | : [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/main/gr-analog/lib/frequency_modulator_fc_impl.cc frequency_modulator_fc_impl.cc] | ||
; Header files | ; Header files | ||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio | : [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/main/gr-analog/lib/frequency_modulator_fc_impl.h frequency_modulator_fc_impl.h] | ||
; Public header files | ; Public header files | ||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio | : [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/main/gr-analog/include/gnuradio/analog/frequency_modulator_fc.h frequency_modulator_fc.h] | ||
; Block definition | ; Block definition | ||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio | : [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/main/gr-analog/grc/analog_frequency_modulator_fc.block.yml analog_frequency_modulator_fc.block.yml] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:03, 4 April 2024
This block is an input amplitude controlled complex sine. It outputs a signal, which has a momentary phase increase that is proportional to sensitivity and input amplitude.
More specifically, takes a real, baseband signal (x_m[n]) and output a frequency modulated signal (y[n]) according to:
Where x[n] is the input sample at time n and is the frequency deviation. Common values for are 5 kHz for narrowband FM channels such as for voice systems and 75 kHz for wideband FM, like audio broadcast FM stations. In this block, the input argument is sensitivity, not the frequency deviation. The sensitivity specifies how much the phase changes based on the new input sample. Given a maximum deviation , and sample rate , the sensitivity is defined as:
Parameters
(R): Run-time adjustable
- Sensitivity (R)
- Sensitivity = (2 * math.pi * deviation) / sample_rate
- where 'deviation' is the change of the frequency when the input is at the values of -1 or +1. If the input is outside [-1, +1], it can deviate more.
Example Flowgraph
Source Files
- C++ files
- frequency_modulator_fc_impl.cc
- Header files
- frequency_modulator_fc_impl.h
- Public header files
- frequency_modulator_fc.h
- Block definition
- analog_frequency_modulator_fc.block.yml