Protocol Formatter: Difference between revisions
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
: The format object to use when reading the header. This block uses a format object derived from a header_format_base class. | : The format object to use when reading the header. This block uses a format object derived from a header_format_base class. | ||
; Length | ; Length tag name | ||
: The tagged stream | : The name for the length tag to be assigned to the tagged stream. | ||
== Example Flowgraph == | == Example Flowgraph == | ||
Latest revision as of 09:41, 13 April 2022
Uses a header format object to create a header from a tagged stream packet.
This block takes in tagged stream and creates a header, generally for MAC-level processing. Each received tagged stream is assumed to be its own frame, so any fragmentation would be done upstream in or before the flowgraph.
The header that is created and transmitted from this block. The payload should then be sent as a parallel tagged stream to be muxed together later. The header is based entirely on the object, which is an object derived from the header_format_base class. All of these packet header format objects operate the same: they take in the payload data as well as possible extra metadata info about the PDU; the format object then returns the output and metadata info. This block then transmits the header vector and attaches and metadata as tags at the start of the header.
Parameters
- Format Obj.
- The format object to use when reading the header. This block uses a format object derived from a header_format_base class.
- Length tag name
- The name for the length tag to be assigned to the tagged stream.
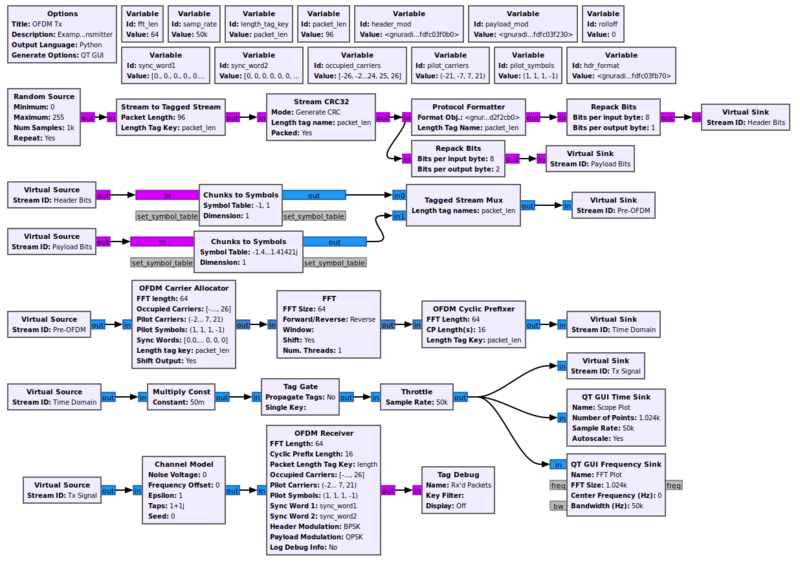
Example Flowgraph
This flowgraph can be found at [1].
Source Files
- C++ files
- protocol_formatter_bb_impl.cc
- Header files
- protocol_formatter_bb_impl.h
- Public header files
- protocol_formatter_bb.h
- Block definition
- digital_protocol_formatter_bb.block.yml