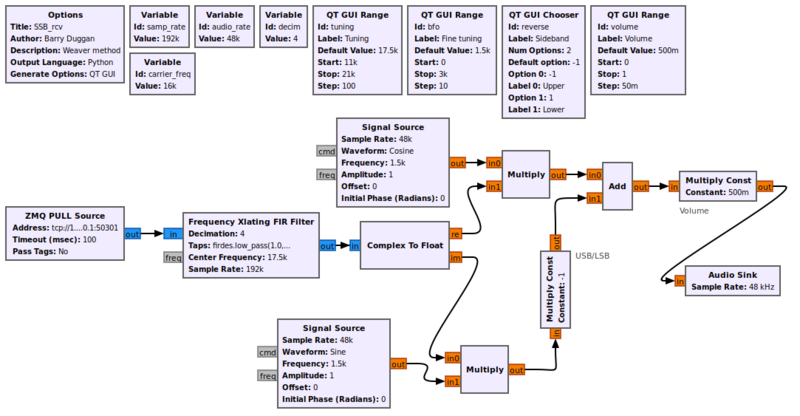
Simulation example: Single Sideband transceiver
UNDER CONSTRUCTION
The first section of this tutorial explains how a Single Sideband (SSB) signal can be created. Rather than using any real hardware for transmission, the signal is sent via a socket to the second section of the tutorial which explains how to demodulate the received signal. The only actual hardware involved is the computer's microphone input and speaker output. In the case of a Raspberry Pi computer, which has no microphone input, an alternative is presented.
This tutorial can be performed with either GNU Radio (GR) version 3.7 or 3.8 (and later). The Graphical User Interface gnuradio-companion (GRC) is used to create a flowgraph for each section.
Prerequisites
SSB transmitter
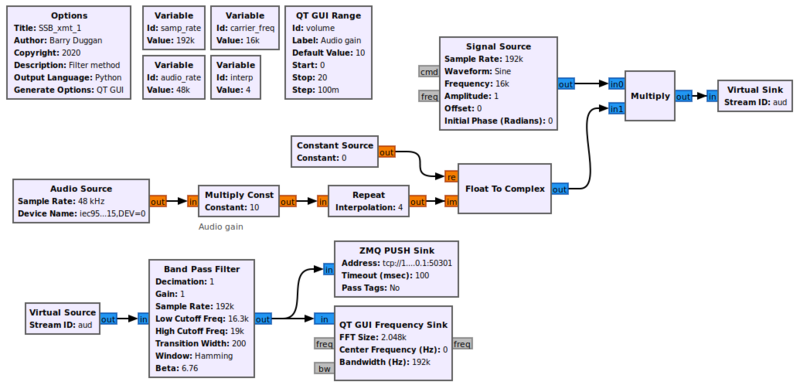
Using gnuradio-companion (GRC) and the following Block descriptions, build this flowgraph of the transmitter section: