WBFM Receive: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
(corrected flowgraph) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Block Docs]] | [[Category:Block Docs]] | ||
Hierarchical block for demodulating a broadcast FM signal. | |||
The input is the downconverted complex baseband signal (gr_complex). | |||
The output is the demodulated audio (float). | |||
Compared to [[WBFM Receive PLL]], this one does a simple mono demodulation with deemphasis | |||
== Parameters == | == Parameters == | ||
; | ; Channel Rate | ||
: | : Input sample rate of complex baseband input. (float) | ||
; Audio Decimation | ; Audio Decimation | ||
: | : How much to decimate Channel Rate to get to audio. (integer) | ||
; Deviation | |||
: FM modulation deviation. Standard broadcast FM uses 75kHz | |||
; Audio Pass | |||
: Low pass filter rolloff frequency | |||
; Audio Stop | |||
: Low pass filter cutoff frequency | |||
; Gain | |||
: Audio gain | |||
; Tau | |||
: Preemphasis time constant (float) - typically 75e-6 | |||
== Example Flowgraph == | == Example Flowgraph == | ||
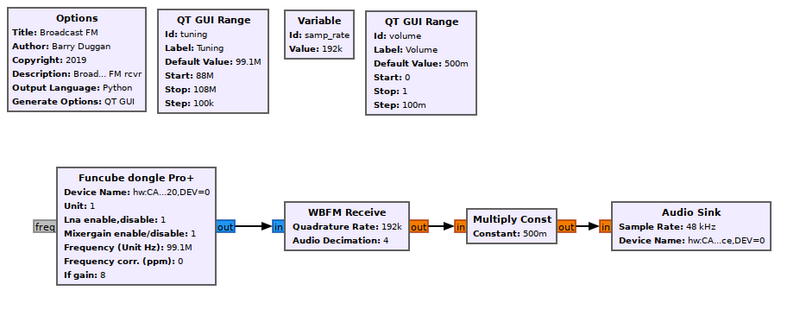
Implementing an FM broadcast band receiver is really easy with the WBFM Receive Block. | |||
[[File:Broadcast_FM_fg.png|800px]] | |||
== Source Files == | == Source Files == | ||
; | ; Python files | ||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio | : [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/master/gr-analog/python/analog/wfm_rcv.py] | ||
; Block definition | ; Block definition | ||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio | : [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/master/gr-analog/grc/analog_wfm_rcv.block.yml] | ||
Revision as of 15:38, 20 August 2020
Hierarchical block for demodulating a broadcast FM signal.
The input is the downconverted complex baseband signal (gr_complex).
The output is the demodulated audio (float).
Compared to WBFM Receive PLL, this one does a simple mono demodulation with deemphasis
Parameters
- Channel Rate
- Input sample rate of complex baseband input. (float)
- Audio Decimation
- How much to decimate Channel Rate to get to audio. (integer)
- Deviation
- FM modulation deviation. Standard broadcast FM uses 75kHz
- Audio Pass
- Low pass filter rolloff frequency
- Audio Stop
- Low pass filter cutoff frequency
- Gain
- Audio gain
- Tau
- Preemphasis time constant (float) - typically 75e-6
Example Flowgraph
Implementing an FM broadcast band receiver is really easy with the WBFM Receive Block.
Source Files
- Python files
- [1]
- Block definition
- [2]