Unpack K Bits: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(add Example Flowgraph) |
|||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
== Parameters == | == Parameters == | ||
; K | ; K | ||
: | : Constant for unpacking bits | ||
== Example Flowgraph == | == Example Flowgraph == | ||
Revision as of 13:04, 19 January 2022
Opposite of Pack K Bits - Converts a byte with k relevant bits to k output bytes with 1 bit each, located in the LSB.
In other words, this block picks the K least significant bits from a byte, and expands them into K bytes of 0 or 1.
Example:
k = 4
in = [0xf5, 0x08]
out = [0,1,0,1,1,0,0,0]
Each input byte produced four output bytes (that are either 0 or 1). Remember that there is no item type of "bit" in GNU Radio, so we have to use bytes to represent single bits.
Parameters
- K
- Constant for unpacking bits
Example Flowgraph
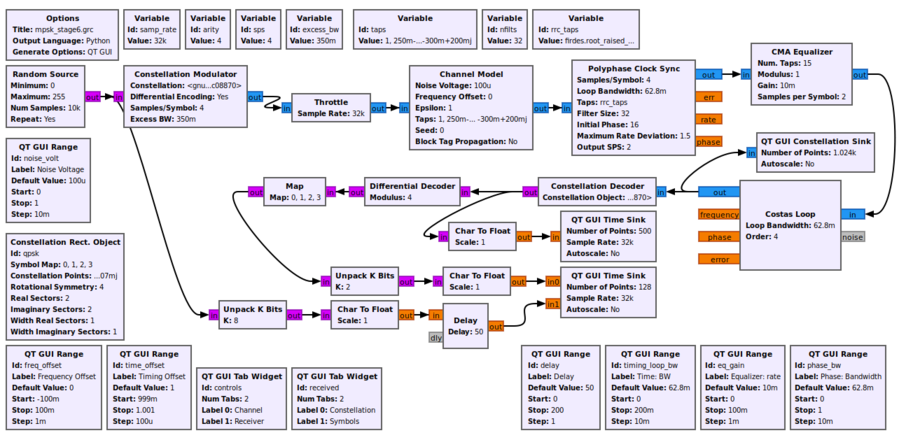
This flowgraph is taken from the Guided_Tutorial_PSK_Demodulation tutorial.