GFSK Demod: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "Category:Block Docs Category:Stub Docs This is the template for the "Page-per-block Docs". This first section should describe what the block...") |
No edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Block Docs]] | [[Category:Block Docs]] | ||
Hierarchical block for Gaussian Frequency Shift Key (GFSK) demodulation. | |||
The input is the complex modulated signal at baseband. | |||
The output is a stream of bits unpacked, 1 bit per byte (the LSB) | |||
== Parameters == | |||
; Samples/Symbol | |||
: Samples per baud >= 2 (integer) | |||
; Sensitivity | |||
: Given to the [[Quadrature Demod]] | |||
; Gain Mu | |||
: Controls rate of mu adjustment | |||
; Mu | |||
: Fractional delay [0.0, 1.0] | |||
; Omega Relative Limit | |||
( | : Sets max variation in omega (float, typically 0.000200 (200 ppm)) | ||
; Freq Error | |||
: Bit rate error as a fraction | |||
; | ; Verbose | ||
: | : Print information about modulator? | ||
; | ; Log | ||
: | : Print modualtion data to files? (bool) | ||
== Example Flowgraph == | == Example Flowgraph == | ||
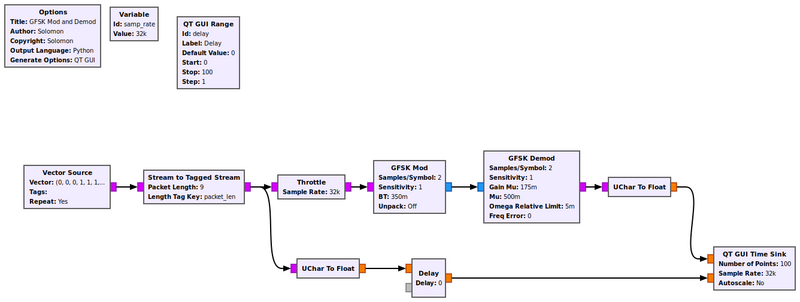
The flowgraph below shows an example of the GFSK Mod and GFSK Demod blocks in action. We GFSK modulate 9-bit long bit stream '000111011', and then GFSK demodulate it. Then we compare the two bit streams to make sure that they are the same. | |||
[[File:Gfsk_mod_and_demod.png|800px]] | |||
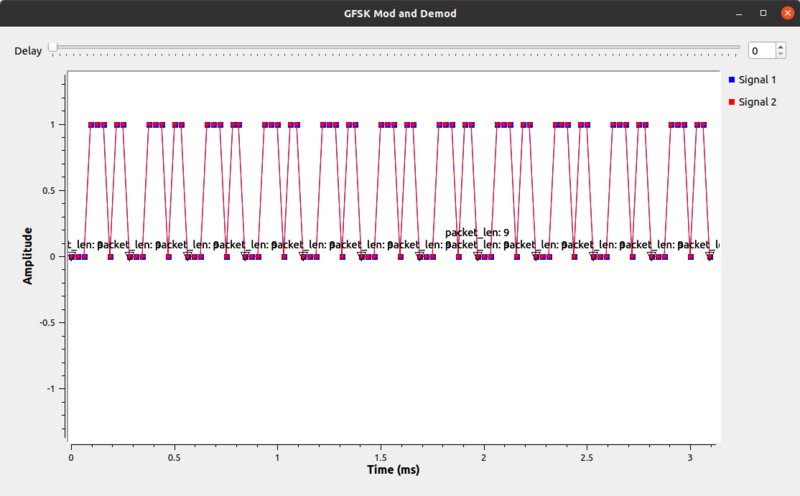
When the flowgraph runs, we see that the red and blue signals are the same, meaning that the bit streams before and after the GFSK modulation and demodulation are the same. | |||
In order to replicate the results shown below, make sure you do the following: | |||
# Make sure you have a vector of 9 bits in your vector source. For example, I used (0,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,1) in this example. | |||
# Make sure you turn off the unpack function in the GFSK Mod block. You will need to double click the block to bring up the Properties pop-up in order to turn it off. Turn it off. Then you will see "Unpack: Off" show up on the block after you close its Properties pop-up. | |||
[[File:Gfsk_mod_and_demod_in_action.png|800px]] | |||
== Source Files == | |||
; | ; Python files | ||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio | : [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/master/gr-digital/python/digital/gfsk.py] | ||
; Block definition | ; Block definition | ||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio | : [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/master/gr-digital/grc/digital_gfsk_demod.block.yml] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:45, 4 April 2022
Hierarchical block for Gaussian Frequency Shift Key (GFSK) demodulation.
The input is the complex modulated signal at baseband.
The output is a stream of bits unpacked, 1 bit per byte (the LSB)
Parameters
- Samples/Symbol
- Samples per baud >= 2 (integer)
- Sensitivity
- Given to the Quadrature Demod
- Gain Mu
- Controls rate of mu adjustment
- Mu
- Fractional delay [0.0, 1.0]
- Omega Relative Limit
- Sets max variation in omega (float, typically 0.000200 (200 ppm))
- Freq Error
- Bit rate error as a fraction
- Verbose
- Print information about modulator?
- Log
- Print modualtion data to files? (bool)
Example Flowgraph
The flowgraph below shows an example of the GFSK Mod and GFSK Demod blocks in action. We GFSK modulate 9-bit long bit stream '000111011', and then GFSK demodulate it. Then we compare the two bit streams to make sure that they are the same.
When the flowgraph runs, we see that the red and blue signals are the same, meaning that the bit streams before and after the GFSK modulation and demodulation are the same.
In order to replicate the results shown below, make sure you do the following:
- Make sure you have a vector of 9 bits in your vector source. For example, I used (0,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,1) in this example.
- Make sure you turn off the unpack function in the GFSK Mod block. You will need to double click the block to bring up the Properties pop-up in order to turn it off. Turn it off. Then you will see "Unpack: Off" show up on the block after you close its Properties pop-up.
Source Files
- Python files
- [1]
- Block definition
- [2]