Phase Shift: Difference between revisions
Jesternofool (talk | contribs) (Removed "Stub" category) |
Jesternofool (talk | contribs) (Added links for C++ and header files) |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
; C++ files | ; C++ files | ||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio | : [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/main/gr-blocks/lib/peak_detector_impl.cc] | ||
; Header files | ; Header files | ||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio | : [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/main/gr-blocks/lib/phase_shift_impl.h] | ||
; Public header files | ; Public header files | ||
Revision as of 00:38, 13 April 2024
This block will phase shift the input signal by the specified phase by multiplying the input times a shift value:
gr_complex(cos(d_shift_in_radians),sin(d_shift_in_radians))
Notes:
If degrees are provided, the block automatically handles the conversion.
This block functions like a Multiply Constant, but with the constant set to ej·shift, i.e. the corresponding value on the complex unit circle.
Parameters
(R): Run-time adjustable
- Phase Shift
- default: '0.0'
- Units
- options: ['Radians', 'Degrees']
Example Flowgraph
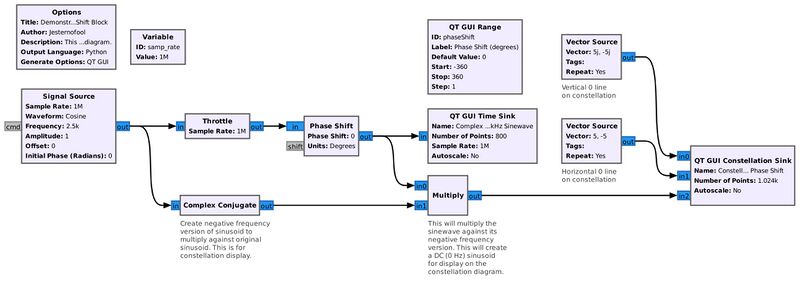
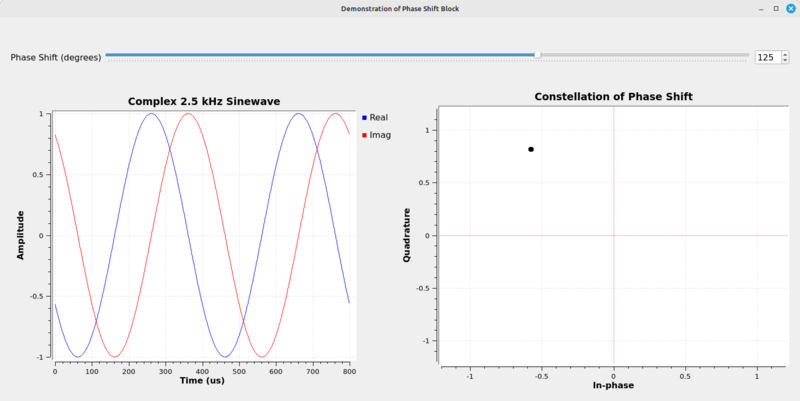
This flowgraph demonstrates how the Phase Shift block will change the phase of a complex sinusoid. It also demonstrates how shifting the phase will change its appearance on a constellation diagram. It creates a complex sinusoid (the Signal Source block), runs the sinusoid through the Phase Shift block, then into a QT GUI Time Sink for display of the time domain of the signal. The phase within the Phase Shift block is controlled by a QT GUI Range block. The range block allows the phase to be adjustable between -360 to +360 degrees (-2 π to +2 π).
Along with that is a Complex Conjugate block that is used to show the phase in the QT GUI Constellation Sink. (NOTE: If the signal going into the constellation or Argand diagram is not at 0 Hz, or centered around 0 Hz, it will spin. This makes it impossible to see the actual phase.) By multiplying the phase-shifted sinusoid with its non-phase-shifted complex conjugate, we can see the phase shift as the range value is adjusted. Two Vector Source blocks create a more-visible cross bar showing the real and imaginary axes.
Gnu Radio blocks used for this demonstration: Signal Source, Complex Conjugate, QT GUI Time Sink, QT GUI Range, Variable, Vector Source, Multiply, QT GUI Constellation Sink
Source Files
- C++ files
- [1]
- Header files
- [2]
- Public header files
- TODO
- Block definition
- blocks_phase_shift.block.yml