Rotator: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Block Docs]] | [[Category:Block Docs]] | ||
Makes a complex rotator block. The phase increment (in radians) is how much phase will be added to the input every value. | Makes a complex rotator block. The phase increment (in radians) is how much phase will be added to the input every value. | ||
== Parameters == | == Parameters == | ||
(''R''): <span class="plainlinks">[https://wiki.gnuradio.org/index.php/GNURadioCompanion#Variable_Controls ''Run-time adjustable'']</span> | (''R''): <span class="plainlinks">[https://wiki.gnuradio.org/index.php/GNURadioCompanion#Variable_Controls ''Run-time adjustable'']</span> | ||
; | ; Phase Increment (''R'') | ||
: | : Acts as the rotational velocity. | ||
== Example Flowgraph == | == Example Flowgraph == | ||
Revision as of 04:56, 21 July 2019
Makes a complex rotator block. The phase increment (in radians) is how much phase will be added to the input every value.
Parameters
(R): Run-time adjustable
- Phase Increment (R)
- Acts as the rotational velocity.
Example Flowgraph
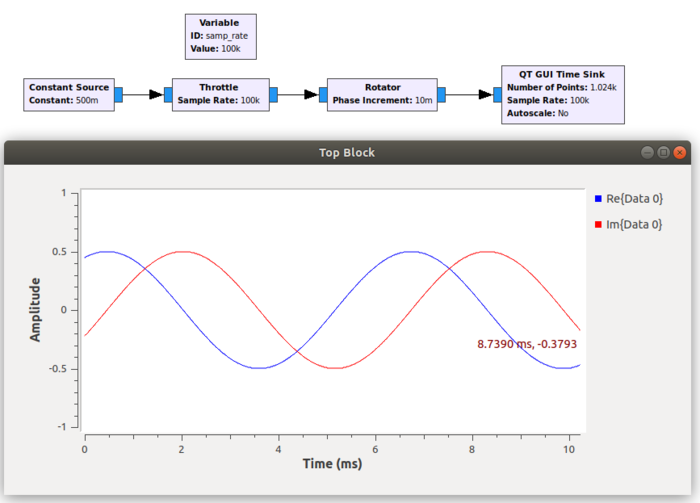
In the example below a constant source, set to 0.5, is fed into the rotator, thus producing a sine wave. The phase increment is set to 0.01 radians and the sample rate is 100kHz, so that equates to 1000 radians every second, or 1000/(2pi) = 159 cycles per second. This corresponds to a period of about 6ms, as shown in the time sink.
Source Files
- C++ files
- TODO
- Header files
- TODO
- Public header files
- TODO
- Block definition
- TODO