Unpacked to Packed: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
(add Example Flowgraph) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Block Docs]] | [[Category:Block Docs]] | ||
Convert a stream of unpacked bytes or shorts into a stream of packed bytes or shorts. | Convert a stream of unpacked bytes or shorts into a stream of packed bytes or shorts. | ||
This is the inverse of [[Packed to Unpacked]] | This is the inverse of [[Packed to Unpacked]] | ||
The low | The low bits are extracted from each input byte or short. These bits are then packed densely into the output bytes or shorts, such that all 8 or 16 bits of the output bytes or shorts are filled with valid input bits. | ||
== Parameters == | == Parameters == | ||
; Bits per Chunk | |||
: Number of bits to pack into each group | |||
; | ; Endianness | ||
: | : Most or Least Significant Bit first | ||
; | ; Num Ports | ||
: | : Number of input streams to operate on | ||
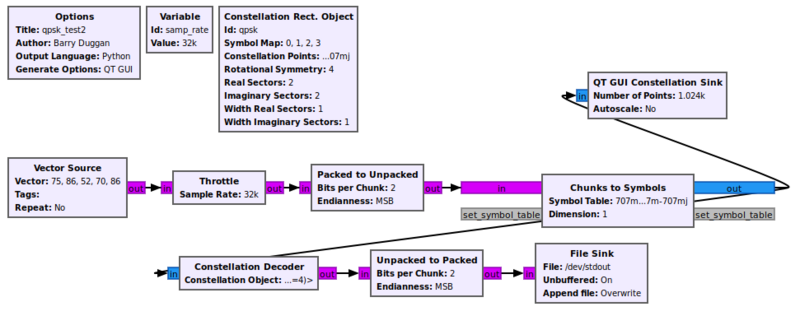
== Example Flowgraph == | == Example Flowgraph == | ||
[[File:Qpsk_test2.png|800px]] | |||
[[File: | |||
== Source Files == | == Source Files == | ||
Latest revision as of 14:42, 6 June 2020
Convert a stream of unpacked bytes or shorts into a stream of packed bytes or shorts.
This is the inverse of Packed to Unpacked
The low bits are extracted from each input byte or short. These bits are then packed densely into the output bytes or shorts, such that all 8 or 16 bits of the output bytes or shorts are filled with valid input bits.
Parameters
- Bits per Chunk
- Number of bits to pack into each group
- Endianness
- Most or Least Significant Bit first
- Num Ports
- Number of input streams to operate on