Creating Python OOT with gr-modtool: Difference between revisions
Mattcarrick (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
|||
| (134 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
This tutorial describes how to create a custom Python block or Out-of-Tree (OOT) module and use it in a flowgraph with the following steps: | |||
* Create an out-of-tree module using ''gr_modtool'' | |||
* Create a new Python block using ''gr_modtool'' | |||
* Modify the Python code in a text editor so the block will function | |||
* Modify the YAML file so it can be displayed in Gnuradio Companion (GRC) | |||
* Install and run the block in a flowgraph | |||
An Out-Of-Tree (OOT) module is a GNU Radio component that does not live within the GNU Radio source tree. The tree is the group of blocks already provided by GNU Radio. Thus, an OOT block is a custom block created to extend GNU Radio with specific functions desired. OOT blocks allow you to maintain the code yourself and have additional functionality alongside the main code. Their functionality can be defined in Python or in C++. Their configuration is described via a yaml file. | |||
A tutorial on using the ''Embedded Python Block'' in GRC is on the [[Creating_Your_First_Block|Creating Your First Block]] page. There are also additional tutorials [[Python_Block_Message_Passing|on using tags]], how to do [[Python_Block_Message_Passing|message passing]] and [[Python_Block_with_Vectors|adding vector inputs and outputs]] in Python blocks that will work for both the ''Embedded Python Block'' and OOT Python blocks. | |||
The next tutorial, [[Creating_C++_OOT_with_gr-modtool|Creating C++ OOT with gr-modtool]], describes how to build a custom C++ OOT module. The C++ OOT tutorial builds upon this Python one, so it is is suggested to at least complete the ''Creating an OOT Module'' portion before moving on. | |||
== Installation Note == | |||
Move into the directory: | This tutorial was written using GNU Radio v3.10.1.1 on Ubuntu 21.10, installed using the Ubuntu PPA from the [[InstallingGR|Installation Wiki Page]]. The basic GNU Radio install using: | ||
<pre>$ cd gr- | |||
<pre>$ sudo apt-get install gnuradio</pre> | |||
does not come with the proper libraries needed to compile and install OOT modules. Consider installing the following packages before continuing: | |||
<pre>$ sudo apt-get install gnuradio-dev cmake libspdlog-dev clang-format</pre> | |||
== Creating an OOT Module == | |||
Open a terminal and navigate to an appropriate directory for writing software, such as the home directory: | |||
<pre>$ cd $HOME</pre> | |||
GNU Radio comes packaged with ''gr_modtool'', a software tool used to create out-of-tree (OOT) modules. An OOT module can be thought of as a collection of custom GNU Radio blocks. Create an OOT module named ''customModule'' using ''gr_modtool'': | |||
<pre>$ gr_modtool newmod customModule</pre> | |||
The directory ''gr-customModule'' is created which contains all of the skeleton code for an OOT module, however it does not yet have any blocks. Move into the ''gr-customModule'' directory: | |||
<pre>$ cd gr-customModule</pre> | |||
List all of the files and directories within the OOT module: | List all of the files and directories within the OOT module: | ||
| Line 17: | Line 39: | ||
The directory listing will be as follows: | The directory listing will be as follows: | ||
apps/ cmake/ CMakeLists.txt docs/ examples/ grc/ include/ lib/ MANIFEST. | <pre>apps/ cmake/ CMakeLists.txt docs/ examples/ grc/ include/ lib/ MANIFEST.yml python/</pre> | ||
== Creating an OOT Block == | |||
Now a block needs to be created within gr-customModule. The custom block will either add or subtract based on an input parameter, so the block is named ''addSubSelect'': | |||
<pre>$ gr_modtool add addSubSelect</pre> | |||
The command will start a questionnaire about how to the block is to be defined: what block type, language and parameters: | |||
<pre>GNU Radio module name identified: customModule | |||
('sink', 'source', 'sync', 'decimator', 'interpolator', 'general', 'tagged_stream', 'hier', 'noblock')</pre> | |||
Select the ''sync'' block, which produces an output for every input: | |||
<pre>Enter block type: sync</pre> | |||
Enter ''python'' as the language: | |||
<pre>Language (python/cpp): python | |||
Language: Python | |||
Block/code identifier: addSubSelect</pre> | |||
Enter the name or organization of the copyright holder: | |||
<pre>Please specify the copyright holder: YourName</pre> | |||
Now enter the argument list: | |||
<pre>Enter valid argument list, including default arguments:</pre> | |||
Enter the argument list as if writing the Python code directly. In this case the ''selector'' will determine whether or not the block performs addition or subtraction. A default argument of ''True'' is given: | |||
<pre>selector=True</pre> | |||
Determine whether or not you want the Python quality assurance (QA) code: | |||
<pre>Add Python QA code? [Y/n] n</pre> | |||
New files will be generated: | |||
<pre>Adding file 'python/customModule/addSubSelect.py'... | |||
Adding file 'grc/customModule_addSubSelect.block.yml'... | |||
Editing grc/CMakeLists.txt...</pre> | |||
Two new files were created, ''addSubSelect.py'' which defines the operation of the block and ''customModule_addSubSelect.block.yml'' which defines the interface of the block for GNU Radio Companion (GRC). The ''CMakeLists.txt'' file was modified so the two files will be installed when the module is compiled and installed. | |||
== Modifying the Python .py File == | |||
Open the python file with a text editor: | |||
<pre>python/customModule/addSubSelect.py </pre> | |||
The following code will be listed: <syntaxhighlight lang="python" line> | |||
#!/usr/bin/env python | |||
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- | |||
# | |||
# Copyright 2022 YourName. | |||
# | |||
# SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-3.0-or-later | |||
# | |||
import numpy | |||
from gnuradio import gr | |||
class addSubSelect(gr.sync_block): | |||
""" | |||
docstring for block addSubSelect | |||
""" | |||
def __init__(self, selector=True): | |||
gr.sync_block.__init__(self, | |||
name="addSubSelect", | |||
in_sig=[<+numpy.float32+>, ], | |||
out_sig=[<+numpy.float32+>, ]) | |||
def work(self, input_items, output_items): | |||
in0 = input_items[0] | |||
out = output_items[0] | |||
# <+signal processing here+> | |||
out[:] = in0 | |||
return len(output_items[0])</syntaxhighlight> | |||
Change the ''import'' statement: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="python" line> | |||
import numpy as np | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
Both the ''__init__()'' function and ''work()'' function need to be modified. The ''__init__()'' function is modified to define the input type. The ''addSubSelect'' block will accept two complex inputs and produce a complex output, therefore the ''in_sig'' and ''out_sig'' parameters need to be changed. The ''selector'' parameter also needs to be saved as a member variable: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="python" line> | |||
def __init__(self, selector=True): | |||
gr.sync_block.__init__(self, | |||
name="addSubSelect", | |||
in_sig=[np.complex64,np.complex64], | |||
out_sig=[np.complex64]) | |||
self.selector = selector</syntaxhighlight> | |||
The ''work()'' function is modified to either add or subtract the two inputs based on the ''selector'' parameter: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="python" line> | |||
def work(self, input_items, output_items): | |||
in0 = input_items[0] | |||
in1 = input_items[1] | |||
if (self.selector): | |||
output_items[0][:] = in0 + in1 | |||
else: | |||
output_items[0][:] = in0 - in1 | |||
return len(output_items[0])</syntaxhighlight> | |||
Save the file. | |||
== Modifying YAML .yml File == | |||
Open the .yml file with a text editor: | |||
<pre>grc/customModule_addSubSelect.block.yml </pre> | |||
The following YAML is displayed: <syntaxhighlight lang="yaml" line> | |||
id: customModule_addSubSelect | |||
label: addSubSelect | |||
category: '[customModule]' | |||
templates: | |||
imports: from gnuradio import customModule | |||
make: customModule.addSubSelect(${selector}) | |||
# Make one 'parameters' list entry for every parameter you want settable from the GUI. | |||
# Keys include: | |||
# * id (makes the value accessible as keyname, e.g. in the make entry) | |||
# * label (label shown in the GUI) | |||
# * dtype (e.g. int, float, complex, byte, short, xxx_vector, ...) | |||
# * default | |||
parameters: | |||
- id: parametername_replace_me | |||
label: FIX ME: | |||
dtype: string | |||
default: You need to fill in your grc/customModule_addSubSelect.block.yaml | |||
#- id: ... | |||
# label: ... | |||
# dtype: ... | |||
# Make one 'inputs' list entry per input and one 'outputs' list entry per output. | |||
# Keys include: | |||
# * label (an identifier for the GUI) | |||
# * domain (optional - stream or message. Default is stream) | |||
# * dtype (e.g. int, float, complex, byte, short, xxx_vector, ...) | |||
# * vlen (optional - data stream vector length. Default is 1) | |||
# * optional (optional - set to 1 for optional inputs. Default is 0) | |||
inputs: | |||
#- label: ... | |||
# domain: ... | |||
# dtype: ... | |||
# vlen: ... | |||
# optional: ... | |||
outputs: | |||
#- label: ... | |||
# domain: ... | |||
# dtype: ... | |||
# vlen: ... | |||
# optional: ... | |||
# 'file_format' specifies the version of the GRC yml format used in the file | |||
# and should usually not be changed. | |||
file_format: 1</syntaxhighlight> | |||
The YAML file needs to be updated to match the ''addSubSelector.py'' file that was just modified. There is a single parameter, ''selector''. Enter the parameter values according to: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="yaml" line> | |||
parameters: | |||
- id: selector | |||
label: Add (True) or Subtract (False) Selector | |||
dtype: bool | |||
default: True</syntaxhighlight> | |||
The two inputs need to be defined in the YAML: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="yaml" line> | |||
inputs: | |||
- label: in0 | |||
domain: stream | |||
dtype: complex | |||
- label: in1 | |||
domain: stream | |||
dtype: complex | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
The single output needs to be defined: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="yaml" line> | |||
outputs: | |||
- label: out0 | |||
domain: stream | |||
dtype: complex | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
Save the file. | |||
== Compiling and Installing the Block == | |||
In the top level directory of ''gr_customModule'', create a ''build'' directory: | |||
<pre>$ mkdir build</pre> | |||
The directory should look like the following: | |||
<pre>apps/ build/ cmake/ CMakeLists.txt docs/ examples/ grc/ include/ lib/ MANIFEST.yml python/</pre> | |||
Move into the build directory, | |||
<pre>$ cd build</pre> | |||
Then run CMake which will prepare the makefiles: | |||
<pre>cmake ..</pre> | |||
Compile the module: | |||
<pre>$ make</pre> | |||
Install the module with sudo: | |||
<pre>sudo make install</pre> | |||
Multiple files will now be installed: | |||
<pre>[ 0%] Built target pygen_apps_9a6dd | |||
[ 0%] Built target copy_module_for_tests | |||
[100%] Built target pygen_python_customModule_f524f | |||
Install the project... | |||
-- Install configuration: "Release" | |||
-- Installing: /usr/local/lib/cmake/gnuradio-customModule/gnuradio-customModuleConfig.cmake | |||
-- Installing: /usr/local/include/gnuradio/customModule/api.h | |||
-- Installing: /usr/local/lib/python3.9/dist-packages/gnuradio/customModule/__init__.py | |||
-- Installing: /usr/local/lib/python3.9/dist-packages/gnuradio/customModule/addSubSelect.py | |||
-- Installing: /usr/local/lib/python3.9/dist-packages/gnuradio/customModule/__init__.pyc | |||
-- Installing: /usr/local/lib/python3.9/dist-packages/gnuradio/customModule/addSubSelect.pyc | |||
-- Installing: /usr/local/lib/python3.9/dist-packages/gnuradio/customModule/__init__.pyo | |||
-- Installing: /usr/local/lib/python3.9/dist-packages/gnuradio/customModule/addSubSelect.pyo | |||
-- Installing: /usr/local/share/gnuradio/grc/blocks/customModule_addSubSelect.block.yml</pre> | |||
Run ''ldconfig'' to update the linking for the customModule library: | |||
<pre>$ sudo ldconfig </pre> | |||
== Using the Custom Block in a Flowgraph == | |||
Start GNU Radio Companion (GRC): | |||
<pre>$ gnuradio-companion &</pre> | |||
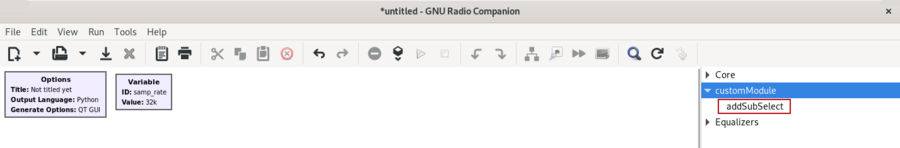
The ''addSubSelect'' block will be available under the ''customModule'' drop down in the block library: | |||
[[File:AddSubSelectInGRC.png|900px]] | |||
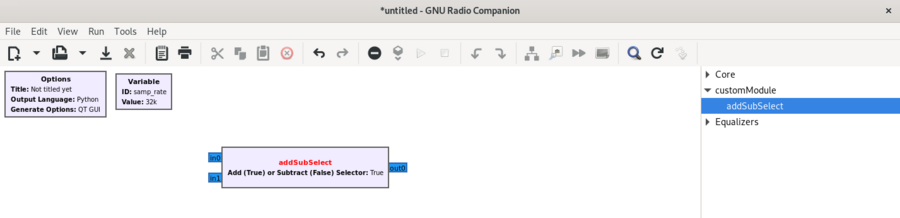
Drag the block into the workspace: | |||
[[File:DragInAddSubSelectBlock.png|900px]] | |||
The block shows the properties as defined in the YAML file: | |||
* Two complex inputs, ''in0'' and ''in1'' | |||
* One complex output, ''out0'' | |||
* A selector parameter | |||
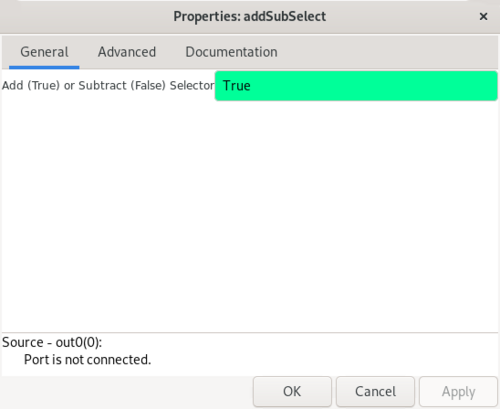
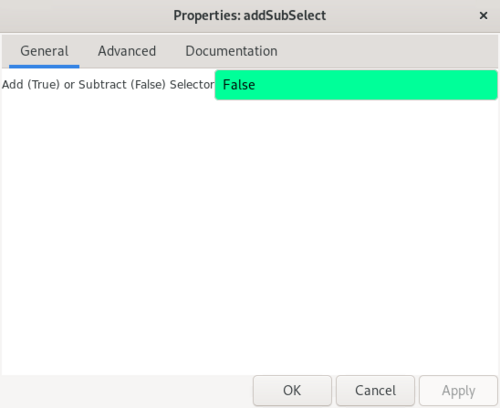
Double-click the block to open the properties. The ''selector'' parameter is described by the label ''Add (True) or Subtract (False) Selector'' with ''True'' as the default value: | |||
[[File:AddSubSelectProperties.png|500px]] | |||
Click OK. | |||
Add the following blocks to the workspace: | |||
* Signal Source | |||
* Constant Source | |||
* Throttle | |||
* QT GUI Time Sink | |||
Update the following parameters | |||
* Signal Source | |||
** Frequency: 100 | |||
** Amplitude: 0.5 | |||
* Constant Source | |||
** Constant: 0.5+0.5j | |||
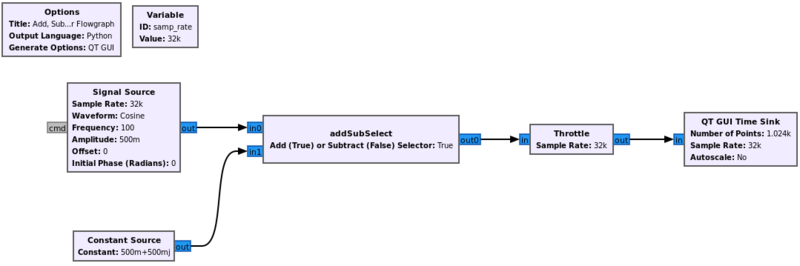
Connect the blocks according to the following flowgraph: | |||
[[File:ConnectAddSubSelectFlowgraph.png|800px]] | |||
== Running the Flowgraph == | |||
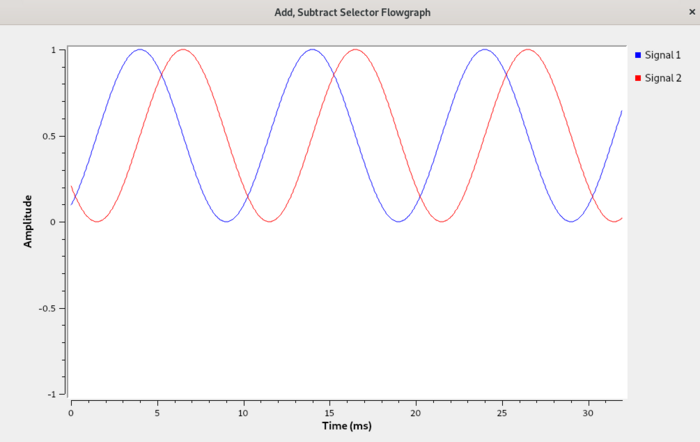
Run the flowgraph. The ''QT GUI Time Sink'' will display the following output, showing the average level of the sinusoid has been raised by ''0.5+0.5j'': | |||
[[File:AddSubSelectPositiveOffset.png|700px]] | |||
Edit the properties off the ''addSubSelect'' block and enter False which enables the subtraction mode: | |||
[[File:AddSubSelectFalse.png|500px]] | |||
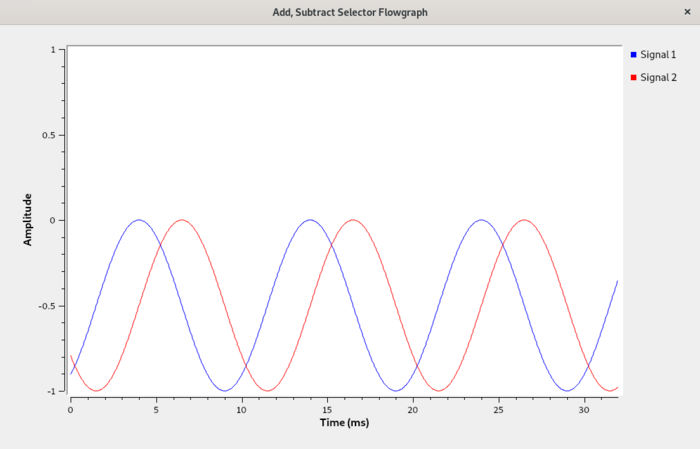
Run the flowgraph. The ''QT GUI Time Sink'' will display the following output, showing the average level of the sinusoid has been reduced by ''0.5+0.5j'': | |||
[[File:AddSubSelectNegativeOffset.png|700px]] | |||
== Making Changes == | |||
It is suggested to recompile and reinstall the module any time a change is made, followed by reloading the block library in GRC. This includes changes such as: | |||
* Number of parameters | |||
* Type of parameters | |||
* Number of input ports or output ports | |||
* Types of input ports or output ports | |||
* Modifying the YAML .yml file | |||
* Modifying the Python .py file | |||
Removing and re-creating the ''build/'' directory may be necessary before recompiling and reinstalling the module depending on the scope of the change: | |||
<pre>$ rm -rf gr-customModule/build | |||
$ mkdir gr-customModule/build</pre> | |||
== Related Tutorial == | |||
The tutorial [[Python_Block_with_Vectors|Python Block with Vectors]] describes how to work with vectors in a Python block. | |||
== Next Tutorial == | |||
The next tutorial, [[Creating_C++_OOT_with_gr-modtool|Creating C++ OOT with gr-modtool]], describes how to build a custom C++ OOT module. | |||
Latest revision as of 18:27, 20 June 2024
This tutorial describes how to create a custom Python block or Out-of-Tree (OOT) module and use it in a flowgraph with the following steps:
- Create an out-of-tree module using gr_modtool
- Create a new Python block using gr_modtool
- Modify the Python code in a text editor so the block will function
- Modify the YAML file so it can be displayed in Gnuradio Companion (GRC)
- Install and run the block in a flowgraph
An Out-Of-Tree (OOT) module is a GNU Radio component that does not live within the GNU Radio source tree. The tree is the group of blocks already provided by GNU Radio. Thus, an OOT block is a custom block created to extend GNU Radio with specific functions desired. OOT blocks allow you to maintain the code yourself and have additional functionality alongside the main code. Their functionality can be defined in Python or in C++. Their configuration is described via a yaml file.
A tutorial on using the Embedded Python Block in GRC is on the Creating Your First Block page. There are also additional tutorials on using tags, how to do message passing and adding vector inputs and outputs in Python blocks that will work for both the Embedded Python Block and OOT Python blocks.
The next tutorial, Creating C++ OOT with gr-modtool, describes how to build a custom C++ OOT module. The C++ OOT tutorial builds upon this Python one, so it is is suggested to at least complete the Creating an OOT Module portion before moving on.
Installation Note
This tutorial was written using GNU Radio v3.10.1.1 on Ubuntu 21.10, installed using the Ubuntu PPA from the Installation Wiki Page. The basic GNU Radio install using:
$ sudo apt-get install gnuradio
does not come with the proper libraries needed to compile and install OOT modules. Consider installing the following packages before continuing:
$ sudo apt-get install gnuradio-dev cmake libspdlog-dev clang-format
Creating an OOT Module
Open a terminal and navigate to an appropriate directory for writing software, such as the home directory:
$ cd $HOME
GNU Radio comes packaged with gr_modtool, a software tool used to create out-of-tree (OOT) modules. An OOT module can be thought of as a collection of custom GNU Radio blocks. Create an OOT module named customModule using gr_modtool:
$ gr_modtool newmod customModule
The directory gr-customModule is created which contains all of the skeleton code for an OOT module, however it does not yet have any blocks. Move into the gr-customModule directory:
$ cd gr-customModule
List all of the files and directories within the OOT module:
$ ls
The directory listing will be as follows:
apps/ cmake/ CMakeLists.txt docs/ examples/ grc/ include/ lib/ MANIFEST.yml python/
Creating an OOT Block
Now a block needs to be created within gr-customModule. The custom block will either add or subtract based on an input parameter, so the block is named addSubSelect:
$ gr_modtool add addSubSelect
The command will start a questionnaire about how to the block is to be defined: what block type, language and parameters:
GNU Radio module name identified: customModule
('sink', 'source', 'sync', 'decimator', 'interpolator', 'general', 'tagged_stream', 'hier', 'noblock')
Select the sync block, which produces an output for every input:
Enter block type: sync
Enter python as the language:
Language (python/cpp): python Language: Python Block/code identifier: addSubSelect
Enter the name or organization of the copyright holder:
Please specify the copyright holder: YourName
Now enter the argument list:
Enter valid argument list, including default arguments:
Enter the argument list as if writing the Python code directly. In this case the selector will determine whether or not the block performs addition or subtraction. A default argument of True is given:
selector=True
Determine whether or not you want the Python quality assurance (QA) code:
Add Python QA code? [Y/n] n
New files will be generated:
Adding file 'python/customModule/addSubSelect.py'... Adding file 'grc/customModule_addSubSelect.block.yml'... Editing grc/CMakeLists.txt...
Two new files were created, addSubSelect.py which defines the operation of the block and customModule_addSubSelect.block.yml which defines the interface of the block for GNU Radio Companion (GRC). The CMakeLists.txt file was modified so the two files will be installed when the module is compiled and installed.
Modifying the Python .py File
Open the python file with a text editor:
python/customModule/addSubSelect.py
The following code will be listed:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
#
# Copyright 2022 YourName.
#
# SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-3.0-or-later
#
import numpy
from gnuradio import gr
class addSubSelect(gr.sync_block):
"""
docstring for block addSubSelect
"""
def __init__(self, selector=True):
gr.sync_block.__init__(self,
name="addSubSelect",
in_sig=[<+numpy.float32+>, ],
out_sig=[<+numpy.float32+>, ])
def work(self, input_items, output_items):
in0 = input_items[0]
out = output_items[0]
# <+signal processing here+>
out[:] = in0
return len(output_items[0])
Change the import statement:
import numpy as np
Both the __init__() function and work() function need to be modified. The __init__() function is modified to define the input type. The addSubSelect block will accept two complex inputs and produce a complex output, therefore the in_sig and out_sig parameters need to be changed. The selector parameter also needs to be saved as a member variable:
def __init__(self, selector=True):
gr.sync_block.__init__(self,
name="addSubSelect",
in_sig=[np.complex64,np.complex64],
out_sig=[np.complex64])
self.selector = selector
The work() function is modified to either add or subtract the two inputs based on the selector parameter:
def work(self, input_items, output_items):
in0 = input_items[0]
in1 = input_items[1]
if (self.selector):
output_items[0][:] = in0 + in1
else:
output_items[0][:] = in0 - in1
return len(output_items[0])
Save the file.
Modifying YAML .yml File
Open the .yml file with a text editor:
grc/customModule_addSubSelect.block.yml
The following YAML is displayed:
id: customModule_addSubSelect
label: addSubSelect
category: '[customModule]'
templates:
imports: from gnuradio import customModule
make: customModule.addSubSelect(${selector})
# Make one 'parameters' list entry for every parameter you want settable from the GUI.
# Keys include:
# * id (makes the value accessible as keyname, e.g. in the make entry)
# * label (label shown in the GUI)
# * dtype (e.g. int, float, complex, byte, short, xxx_vector, ...)
# * default
parameters:
- id: parametername_replace_me
label: FIX ME:
dtype: string
default: You need to fill in your grc/customModule_addSubSelect.block.yaml
#- id: ...
# label: ...
# dtype: ...
# Make one 'inputs' list entry per input and one 'outputs' list entry per output.
# Keys include:
# * label (an identifier for the GUI)
# * domain (optional - stream or message. Default is stream)
# * dtype (e.g. int, float, complex, byte, short, xxx_vector, ...)
# * vlen (optional - data stream vector length. Default is 1)
# * optional (optional - set to 1 for optional inputs. Default is 0)
inputs:
#- label: ...
# domain: ...
# dtype: ...
# vlen: ...
# optional: ...
outputs:
#- label: ...
# domain: ...
# dtype: ...
# vlen: ...
# optional: ...
# 'file_format' specifies the version of the GRC yml format used in the file
# and should usually not be changed.
file_format: 1
The YAML file needs to be updated to match the addSubSelector.py file that was just modified. There is a single parameter, selector. Enter the parameter values according to:
parameters:
- id: selector
label: Add (True) or Subtract (False) Selector
dtype: bool
default: True
The two inputs need to be defined in the YAML:
inputs:
- label: in0
domain: stream
dtype: complex
- label: in1
domain: stream
dtype: complex
The single output needs to be defined:
outputs:
- label: out0
domain: stream
dtype: complex
Save the file.
Compiling and Installing the Block
In the top level directory of gr_customModule, create a build directory:
$ mkdir build
The directory should look like the following:
apps/ build/ cmake/ CMakeLists.txt docs/ examples/ grc/ include/ lib/ MANIFEST.yml python/
Move into the build directory,
$ cd build
Then run CMake which will prepare the makefiles:
cmake ..
Compile the module:
$ make
Install the module with sudo:
sudo make install
Multiple files will now be installed:
[ 0%] Built target pygen_apps_9a6dd [ 0%] Built target copy_module_for_tests [100%] Built target pygen_python_customModule_f524f Install the project... -- Install configuration: "Release" -- Installing: /usr/local/lib/cmake/gnuradio-customModule/gnuradio-customModuleConfig.cmake -- Installing: /usr/local/include/gnuradio/customModule/api.h -- Installing: /usr/local/lib/python3.9/dist-packages/gnuradio/customModule/__init__.py -- Installing: /usr/local/lib/python3.9/dist-packages/gnuradio/customModule/addSubSelect.py -- Installing: /usr/local/lib/python3.9/dist-packages/gnuradio/customModule/__init__.pyc -- Installing: /usr/local/lib/python3.9/dist-packages/gnuradio/customModule/addSubSelect.pyc -- Installing: /usr/local/lib/python3.9/dist-packages/gnuradio/customModule/__init__.pyo -- Installing: /usr/local/lib/python3.9/dist-packages/gnuradio/customModule/addSubSelect.pyo -- Installing: /usr/local/share/gnuradio/grc/blocks/customModule_addSubSelect.block.yml
Run ldconfig to update the linking for the customModule library:
$ sudo ldconfig
Using the Custom Block in a Flowgraph
Start GNU Radio Companion (GRC):
$ gnuradio-companion &
The addSubSelect block will be available under the customModule drop down in the block library:
Drag the block into the workspace:
The block shows the properties as defined in the YAML file:
- Two complex inputs, in0 and in1
- One complex output, out0
- A selector parameter
Double-click the block to open the properties. The selector parameter is described by the label Add (True) or Subtract (False) Selector with True as the default value:
Click OK.
Add the following blocks to the workspace:
- Signal Source
- Constant Source
- Throttle
- QT GUI Time Sink
Update the following parameters
- Signal Source
- Frequency: 100
- Amplitude: 0.5
- Constant Source
- Constant: 0.5+0.5j
Connect the blocks according to the following flowgraph:
Running the Flowgraph
Run the flowgraph. The QT GUI Time Sink will display the following output, showing the average level of the sinusoid has been raised by 0.5+0.5j:
Edit the properties off the addSubSelect block and enter False which enables the subtraction mode:
Run the flowgraph. The QT GUI Time Sink will display the following output, showing the average level of the sinusoid has been reduced by 0.5+0.5j:
Making Changes
It is suggested to recompile and reinstall the module any time a change is made, followed by reloading the block library in GRC. This includes changes such as:
- Number of parameters
- Type of parameters
- Number of input ports or output ports
- Types of input ports or output ports
- Modifying the YAML .yml file
- Modifying the Python .py file
Removing and re-creating the build/ directory may be necessary before recompiling and reinstalling the module depending on the scope of the change:
$ rm -rf gr-customModule/build $ mkdir gr-customModule/build
Related Tutorial
The tutorial Python Block with Vectors describes how to work with vectors in a Python block.
Next Tutorial
The next tutorial, Creating C++ OOT with gr-modtool, describes how to build a custom C++ OOT module.