Moving Average: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
(add Example Flowgraph) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Parameters == | == Parameters == | ||
(''R''): | (''R''): <span class="plainlinks">[https://wiki.gnuradio.org/index.php/GNURadioCompanion#Variable_Controls ''Run-time adjustable'']</span> | ||
; Input Type | ; Input Type | ||
: Complex, Float, Int or Short | : Complex, Float, Int or Short | ||
| Line 30: | Line 29: | ||
== Example Flowgraph == | == Example Flowgraph == | ||
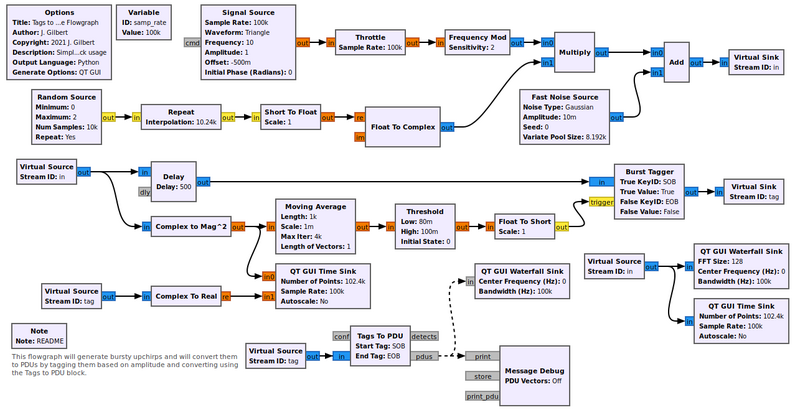
This flowgraph can be found at [https://raw.githubusercontent.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/master/gr-pdu/examples/tags_to_pdu_example.grc] | |||
[[File:Tags_to_pdu_fg.png|800px]] | |||
== Source Files == | == Source Files == | ||
Latest revision as of 12:31, 18 December 2021
Computes a moving average of the input:
Output[i] = scale * sum(input[i-length: i])
In its default parameters, the block actually computes a moving sum.
Parameters
(R): Run-time adjustable
- Input Type
- Complex, Float, Int or Short
- Length (R)
- The size of the moving average window to use.
- Scale (R)
- Factor to scale the sum of the last (Length) samples. To get an actual moving average, the scale should then be set to 1/Length.
- Max Iter
- The maximum number of samples the block will treat in one call of its work function. Larger numbers can improve throughput at the cost of latency and potential numerical instability with float or complex input.
- Max Iter can be smaller than Length without issues.
- vlen
- Used if the input samples are vectors and corresponds to the length of those vectors.
- When operating on vectors, the average is done using only the numbers from the same vector index:
- Output[i][vector_index] = scale * sum(Input[i-length: i][vector_index])
Example Flowgraph
This flowgraph can be found at [1]
Source Files
- C++ files
- All inputs
- Header files
- All inputs
- Public header files
- All inputs
- Block definition
- GRC yaml