Multiply by Matrix: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "Category:Block Docs Category:Stub Docs This is the template for the "Page-per-block Docs". This first section should describe what the block...") |
EngineerLife (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Block Docs]] | [[Category:Block Docs]] | ||
Matrix multiplexer/multiplier: y(k) = A x(k) | |||
This block is similar to [[Multiply Const]], the difference being it can handle several inputs and outputs, and the input-to-output relation can be described by the following mathematical equation: | |||
y(k) = A x(k) | |||
where y in R^n, x in R^m, A in R^n*m | |||
y(k) and x(k) are column-vectors describing the elements on the input port at time step k(this is a sync block with no memory). | |||
Examples for where to use this block include: | |||
* Switch matrices (i.e. switch which ports go where), assuming all ports run on the same rate | |||
* Simulation of static MIMO-Channels (in that case, A is the channel matrix) | |||
* Summing up streams with variable coefficients | |||
This block as one input message port. A message sent to this port will be converted to a std::vector<std::vector<T> >, and then passed on to set_A(). If no conversion is possible, a warning is issued via the logging interface, and A remains unchanged. | |||
Note : It is not possible to change the dimension of the matrix after initialization, as this affects the I/O signature! If a matrix of invalid size is passed to the block, an alert is raised via the logging interface, and A remains unchanged. | |||
[[File:Multiply by Matrix basic visual.png]] | |||
== Parameters == | == Parameters == | ||
(''R''): <span class="plainlinks">[https://wiki.gnuradio.org/index.php/GNURadioCompanion#Variable_Controls ''Run-time adjustable'']</span> | (''R''): <span class="plainlinks">[https://wiki.gnuradio.org/index.php/GNURadioCompanion#Variable_Controls ''Run-time adjustable'']</span> | ||
; | ; Type | ||
: | : Only Complex and Float are supported! | ||
; | ; Matrix A (''R'') | ||
: | : The matrix. Matrix A above would be input as <code>((1, 0, 0), (1, 1,0), (1, 1,1))</code>. | ||
; TPP | |||
: The tag propagation policy. | |||
: '''All to All:''' All input tags are passed to all outputs. | |||
: '''One to One:''' Input tags on input K are passed to output K. | |||
: '''No Propagation:''' No tags are propagated through the block. | |||
: '''Matrix-Defined:''' A tag is propagated from input k to output l, if A(l,k) != 0. | |||
== Example Flowgraph == | == Example Flowgraph == | ||
'''Basic Example''' | |||
A simple example flowgraph would be: | |||
[[File:Multiply by Matrix basic flowgraph.png]] | |||
In this case, the inputs are <code>X_0 = 1; X_1 = 3; X_2=7;</code> from a vector source. | |||
The Matrix is set to match A above. | |||
[[File:Multiply by Matrix basic example settings.png|500px]] | |||
This results in an output <code>Y_0 = 1; Y_1 = 4; Y_2 = 11;</code>. | |||
[[File:Multiply by Matrix Basic Output.png|500px]] | |||
'''Tagging Example''' | |||
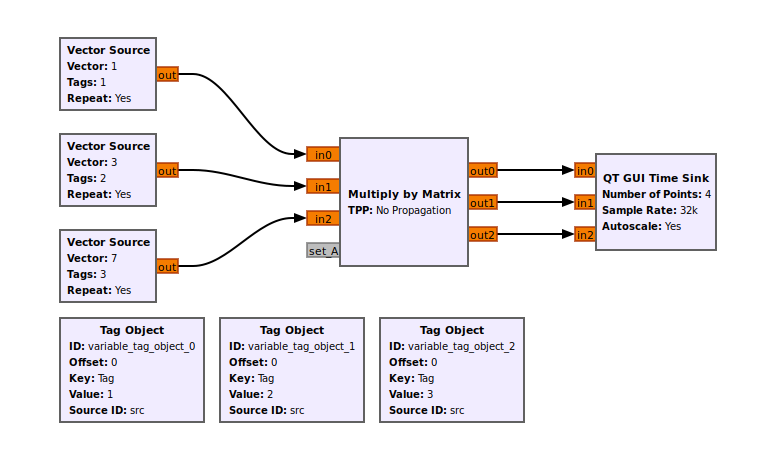
To demonstrate the tag propagation, here is another example: | |||
[[File:Multiply by Matrix tag flowgraph.png]] | |||
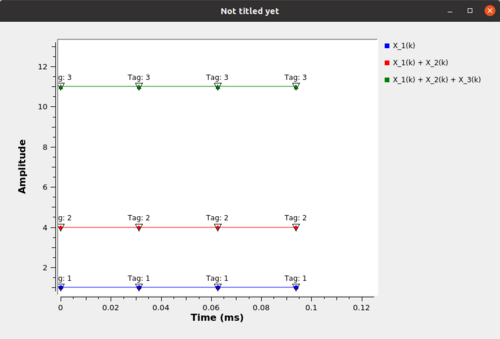
If the '''One to One''' TTP is selected the output tagging would look like: | |||
[[File:Multiply by Matrix tag one to one output.png|500px]] | |||
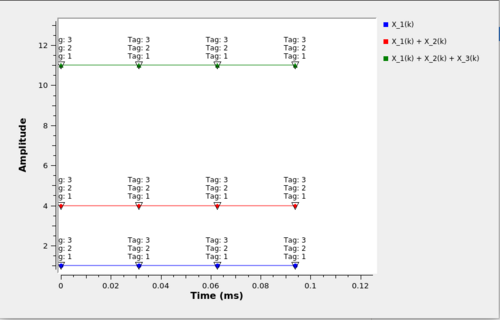
If the '''All to All''' TTP is selected the output tagging would look like: | |||
[[File:Multiply by Matrix All to All tag output.png|500px]] | |||
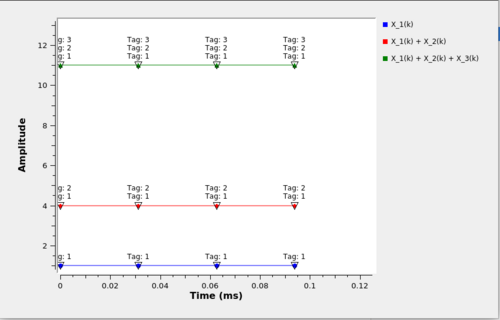
If the '''Matrix-defined''' TTP is selected the output tagging would look like: | |||
[[File:Multiply by Matrix matrix defined tag.png|500px]] | |||
== Source Files == | == Source Files == | ||
; C++ files | ; C++ files | ||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio | : [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/master/gr-blocks/lib/multiply_matrix_impl.cc multiply_matrix_impl.cc] | ||
; Header files | ; Header files | ||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio | : [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/master/gr-blocks/lib/multiply_matrix_impl.h multiply_matrix_impl.h] | ||
; Public header files | ; Public header files | ||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio | : [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/master/gr-blocks/include/gnuradio/blocks/multiply_matrix.h multiply_matrix.h] | ||
; Block definition | ; Block definition | ||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio | : [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/master/gr-blocks/grc/blocks_multiply_matrix_xx.block.yml blocks_multiply_matrix_xx.block.yml] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:42, 6 August 2023
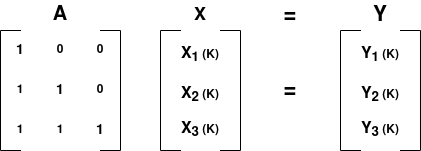
Matrix multiplexer/multiplier: y(k) = A x(k)
This block is similar to Multiply Const, the difference being it can handle several inputs and outputs, and the input-to-output relation can be described by the following mathematical equation: y(k) = A x(k) where y in R^n, x in R^m, A in R^n*m
y(k) and x(k) are column-vectors describing the elements on the input port at time step k(this is a sync block with no memory).
Examples for where to use this block include:
- Switch matrices (i.e. switch which ports go where), assuming all ports run on the same rate
- Simulation of static MIMO-Channels (in that case, A is the channel matrix)
- Summing up streams with variable coefficients
This block as one input message port. A message sent to this port will be converted to a std::vector<std::vector<T> >, and then passed on to set_A(). If no conversion is possible, a warning is issued via the logging interface, and A remains unchanged.
Note : It is not possible to change the dimension of the matrix after initialization, as this affects the I/O signature! If a matrix of invalid size is passed to the block, an alert is raised via the logging interface, and A remains unchanged.
Parameters
(R): Run-time adjustable
- Type
- Only Complex and Float are supported!
- Matrix A (R)
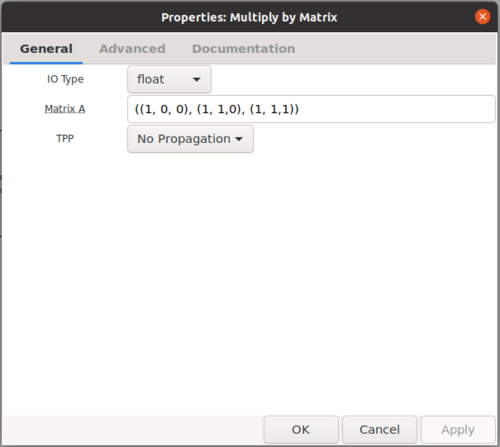
- The matrix. Matrix A above would be input as
((1, 0, 0), (1, 1,0), (1, 1,1)).
- TPP
- The tag propagation policy.
- All to All: All input tags are passed to all outputs.
- One to One: Input tags on input K are passed to output K.
- No Propagation: No tags are propagated through the block.
- Matrix-Defined: A tag is propagated from input k to output l, if A(l,k) != 0.
Example Flowgraph
Basic Example
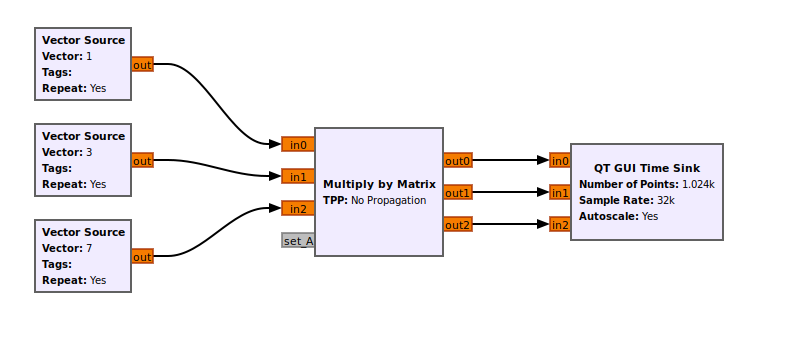
A simple example flowgraph would be:
In this case, the inputs are X_0 = 1; X_1 = 3; X_2=7; from a vector source.
The Matrix is set to match A above.
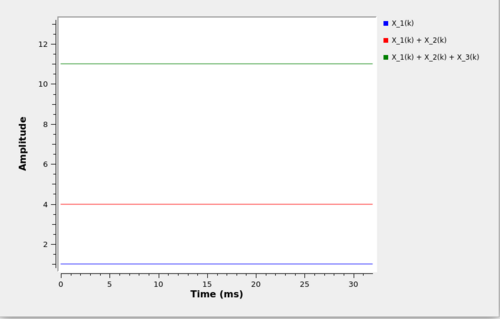
This results in an output Y_0 = 1; Y_1 = 4; Y_2 = 11;.
Tagging Example
To demonstrate the tag propagation, here is another example:
If the One to One TTP is selected the output tagging would look like:
If the All to All TTP is selected the output tagging would look like:
If the Matrix-defined TTP is selected the output tagging would look like:
Source Files
- C++ files
- multiply_matrix_impl.cc
- Header files
- multiply_matrix_impl.h
- Public header files
- multiply_matrix.h
- Block definition
- blocks_multiply_matrix_xx.block.yml