GFSK Mod: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "Category:Block Docs Category:Stub Docs This is the template for the "Page-per-block Docs". This first section should describe what the block...") |
|||
| (26 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Block Docs]] | [[Category:Block Docs]] | ||
Hierarchical block for Gaussian Frequency Shift Key (GFSK) modulation. | |||
The input is a byte stream (unsigned char) and the output is the complex modulated signal at baseband. | |||
== Parameters == | |||
; Samples/Symbol | |||
: Samples per baud >= 2 (integer) | |||
: Default value = 2 | |||
; Sensitivity | |||
: Given to the [[Frequency Mod]] | |||
: Default value = 1.0 | |||
; BT | |||
: Gaussian filter bandwidth * symbol time (float) | |||
: Default value = 0.35 | |||
= | ; Verbose | ||
: Prints the value of bits per symbol and BT | |||
: Default value = Off | |||
; Log | |||
: Prints the following modulation data to .dat files: | |||
: * Chunks to Symbol data is written to "nrz.dat" | |||
: * Output of Gaussian filter is written to "gaussian_filter.dat" | |||
: * Output of frequency modulator is written to "fmmod.dat" | |||
: Default value = Off | |||
; Unpack (depreciated in GNU Radio 3.8) | |||
: Unpack input byte stream? | |||
== Internal Structure == | |||
: | For GNU Radio 3.8: | ||
Packed to unpacked (input:byte, output:byte) --> Chunks to Symbols (input: byte, output: float) --> Interpolating FIR Filter (Float to float(real taps)) --> Frequency Mod --> Multiply const (I/O type:complex) | |||
: | |||
== Example Flowgraph == | == Example Flowgraph == | ||
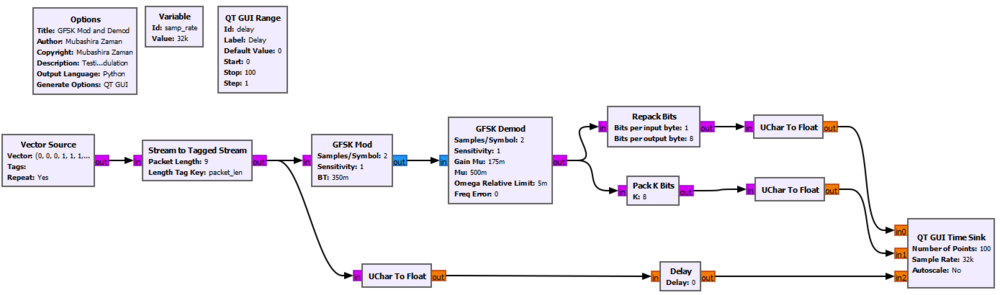
This flowgraph has been created in GNU Radio 3.8. It shows an example of the GFSK Mod and GFSK Demod blocks in action. We GFSK modulate a 9-bit long bit stream '000111011', and then GFSK demodulate it. The input to the GFSK Mod block is in packed format, whereas the output of GFSK Demod block is in unpacked format. We can use the Repack Bits/ Pack K Bits block to convert the output from GFSK Demod to packed format. Both of these options are shown in the following flowchart. All three bit streams are compared in the QT GUI Time Sink block to make sure that they are the same. | |||
== | [[File:GFSK Mod and Demod Example.PNG|1000px]] | ||
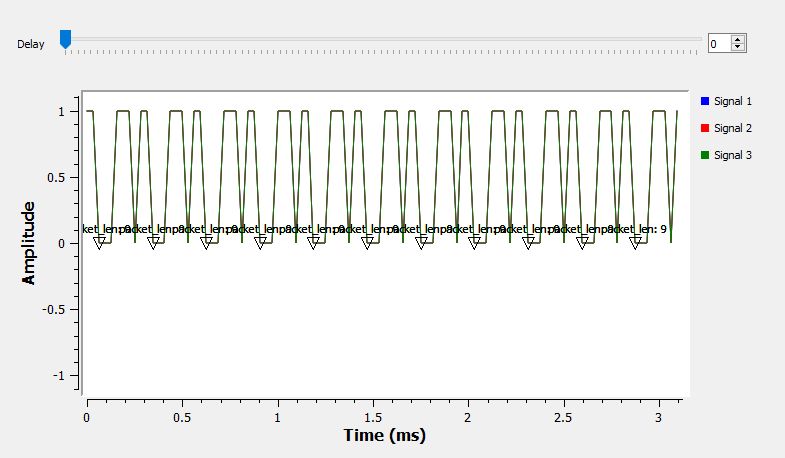
When the flowgraph runs, we see that the red, blue and green signals are the same, meaning that the bit streams before and after the GFSK modulation and demodulation are the same. | |||
In order to replicate the results shown below, make sure you do the following: | |||
# Make sure you have a vector of 9 bits in your vector source. The vector in above example is (0,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,1). | |||
# Create a QT GUI Range block with Id = delay. | |||
# For the Repack Bits block, set the "endianness" value to MSB. | |||
# Match the input and output types of the blocks as shown in the above flowchart (purple = byte, blue = complex, orange = float) | |||
[[File:GFSK Mod and Demod Output.png|800px]] | |||
== Source Files == | |||
; | ; Python files | ||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio | : [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/master/gr-digital/python/digital/gfsk.py] | ||
; Block definition | ; Block definition | ||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio | : [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/master/gr-digital/grc/digital_gfsk_mod.block.yml] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:34, 29 March 2022
Hierarchical block for Gaussian Frequency Shift Key (GFSK) modulation.
The input is a byte stream (unsigned char) and the output is the complex modulated signal at baseband.
Parameters
- Samples/Symbol
- Samples per baud >= 2 (integer)
- Default value = 2
- Sensitivity
- Given to the Frequency Mod
- Default value = 1.0
- BT
- Gaussian filter bandwidth * symbol time (float)
- Default value = 0.35
- Verbose
- Prints the value of bits per symbol and BT
- Default value = Off
- Log
- Prints the following modulation data to .dat files:
- * Chunks to Symbol data is written to "nrz.dat"
- * Output of Gaussian filter is written to "gaussian_filter.dat"
- * Output of frequency modulator is written to "fmmod.dat"
- Default value = Off
- Unpack (depreciated in GNU Radio 3.8)
- Unpack input byte stream?
Internal Structure
For GNU Radio 3.8:
Packed to unpacked (input:byte, output:byte) --> Chunks to Symbols (input: byte, output: float) --> Interpolating FIR Filter (Float to float(real taps)) --> Frequency Mod --> Multiply const (I/O type:complex)
Example Flowgraph
This flowgraph has been created in GNU Radio 3.8. It shows an example of the GFSK Mod and GFSK Demod blocks in action. We GFSK modulate a 9-bit long bit stream '000111011', and then GFSK demodulate it. The input to the GFSK Mod block is in packed format, whereas the output of GFSK Demod block is in unpacked format. We can use the Repack Bits/ Pack K Bits block to convert the output from GFSK Demod to packed format. Both of these options are shown in the following flowchart. All three bit streams are compared in the QT GUI Time Sink block to make sure that they are the same.
When the flowgraph runs, we see that the red, blue and green signals are the same, meaning that the bit streams before and after the GFSK modulation and demodulation are the same.
In order to replicate the results shown below, make sure you do the following:
- Make sure you have a vector of 9 bits in your vector source. The vector in above example is (0,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,1).
- Create a QT GUI Range block with Id = delay.
- For the Repack Bits block, set the "endianness" value to MSB.
- Match the input and output types of the blocks as shown in the above flowchart (purple = byte, blue = complex, orange = float)
Source Files
- Python files
- [1]
- Block definition
- [2]