FLL Band-Edge: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "Category:Block Docs Category:Stub Docs This is the template for the "Page-per-block Docs". This first section should describe what the block...") |
(/* Example Flowgraph update picture) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Block Docs]] | [[Category:Block Docs]] | ||
Frequency Lock Loop using band-edge filters. | |||
The frequency lock loop derives a band-edge filter that covers the upper and lower bandwidths of a digitally-modulated signal. The bandwidth range is determined by the excess bandwidth (e.g., rolloff factor) of the modulated signal. The placement in frequency of the band-edges is determined by the oversampling ratio (number of samples per symbol) and the excess bandwidth. The size of the filters should be fairly large so as to average over a number of symbols. | |||
The FLL works by filtering the upper and lower band edges into x_u(t) and x_l(t), respectively. These are combined to form cc(t) = x_u(t) + x_l(t) and ss(t) = x_u(t) - x_l(t). Combining these to form the signal e(t) = Re{cc(t) \times ss(t)^*} (where ^* is the complex conjugate) provides an error signal at the DC term that is directly proportional to the carrier frequency. We then make a second-order loop using the error signal that is the running average of e(t). | |||
In practice, the above equation can be simplified by just comparing the absolute value squared of the output of both filters: abs(x_l(t))^2 - abs(x_u(t))^2 = norm(x_l(t)) - norm(x_u(t)). | |||
In theory, the band-edge filter is the derivative of the matched filter in frequency, (H_be(f) = frac{H(f)}{df}). In practice, this comes down to a quarter sine wave at the point of the matched filter's rolloff (if it's a raised-cosine, the derivative of a cosine is a sine). Extend this sine by another quarter wave to make a half wave around the band-edges is equivalent in time to the sum of two sinc functions. The baseband filter for the band edges is therefore derived from this sum of sincs. The band edge filters are then just the baseband signal modulated to the correct place in frequency. All of these calculations are done in the 'design_filter' function. | |||
Note: We use FIR filters here because the filters have to have a flat phase response over the entire frequency range to allow their comparisons to be valid. | |||
It is very important that the band edge filters be the derivatives of the pulse shaping filter, and that they be linear phase. Otherwise, the variance of the error will be very large. | |||
== Parameters == | == Parameters == | ||
(''R''): <span class="plainlinks">[https://wiki.gnuradio.org/index.php/GNURadioCompanion#Variable_Controls ''Run-time adjustable'']</span> | (''R''): <span class="plainlinks">[https://wiki.gnuradio.org/index.php/GNURadioCompanion#Variable_Controls ''Run-time adjustable'']</span> | ||
; | ; Samples per symbol | ||
: | : Number of samples per symbol | ||
; Filter rolloff factor | |||
: Rolloff (excess bandwidth) of signal filter | |||
; Prototype filter size | |||
: Number of filter taps to generate | |||
; | ; Loop bandwidth (''R'') | ||
: | : Loop bandwidth | ||
== Example Flowgraph == | == Example Flowgraph == | ||
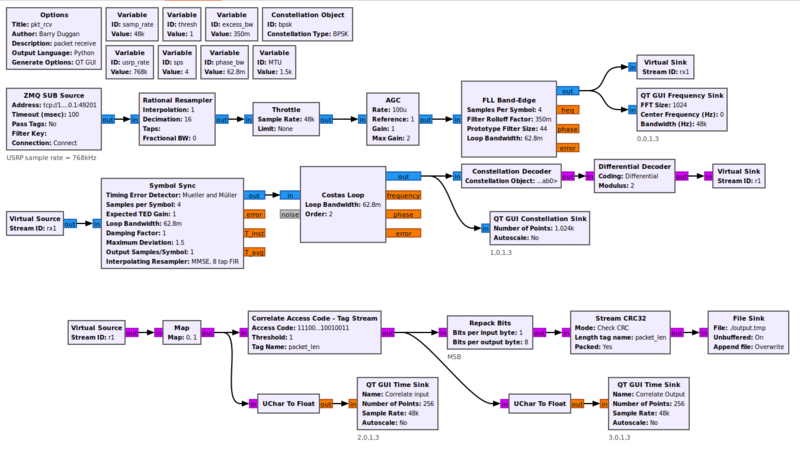
This flowgraph can be found at [https://github.com/duggabe/gr-control/blob/main/Receivers/pkt_rcv.grc]. | |||
[[File:Pkt_rcv_fg.png|800px]] | |||
== Source Files == | == Source Files == | ||
; C++ files | ; C++ files | ||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio | : [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/main/gr-digital/lib/fll_band_edge_cc_impl.cc fll_band_edge_cc_impl.cc] | ||
; Header files | ; Header files | ||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio | : [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/main/gr-digital/lib/fll_band_edge_cc_impl.h fll_band_edge_cc_impl.h] | ||
; Public header files | ; Public header files | ||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio | : [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/main/gr-digital/include/gnuradio/digital/fll_band_edge_cc.h fll_band_edge_cc.h] | ||
; Block definition | ; Block definition | ||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio | : [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/main/gr-digital/grc/digital_fll_band_edge_cc.block.yml digital_fll_band_edge_cc.block.yml] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:23, 15 June 2023
Frequency Lock Loop using band-edge filters.
The frequency lock loop derives a band-edge filter that covers the upper and lower bandwidths of a digitally-modulated signal. The bandwidth range is determined by the excess bandwidth (e.g., rolloff factor) of the modulated signal. The placement in frequency of the band-edges is determined by the oversampling ratio (number of samples per symbol) and the excess bandwidth. The size of the filters should be fairly large so as to average over a number of symbols.
The FLL works by filtering the upper and lower band edges into x_u(t) and x_l(t), respectively. These are combined to form cc(t) = x_u(t) + x_l(t) and ss(t) = x_u(t) - x_l(t). Combining these to form the signal e(t) = Re{cc(t) \times ss(t)^*} (where ^* is the complex conjugate) provides an error signal at the DC term that is directly proportional to the carrier frequency. We then make a second-order loop using the error signal that is the running average of e(t).
In practice, the above equation can be simplified by just comparing the absolute value squared of the output of both filters: abs(x_l(t))^2 - abs(x_u(t))^2 = norm(x_l(t)) - norm(x_u(t)).
In theory, the band-edge filter is the derivative of the matched filter in frequency, (H_be(f) = frac{H(f)}{df}). In practice, this comes down to a quarter sine wave at the point of the matched filter's rolloff (if it's a raised-cosine, the derivative of a cosine is a sine). Extend this sine by another quarter wave to make a half wave around the band-edges is equivalent in time to the sum of two sinc functions. The baseband filter for the band edges is therefore derived from this sum of sincs. The band edge filters are then just the baseband signal modulated to the correct place in frequency. All of these calculations are done in the 'design_filter' function.
Note: We use FIR filters here because the filters have to have a flat phase response over the entire frequency range to allow their comparisons to be valid.
It is very important that the band edge filters be the derivatives of the pulse shaping filter, and that they be linear phase. Otherwise, the variance of the error will be very large.
Parameters
(R): Run-time adjustable
- Samples per symbol
- Number of samples per symbol
- Filter rolloff factor
- Rolloff (excess bandwidth) of signal filter
- Prototype filter size
- Number of filter taps to generate
- Loop bandwidth (R)
- Loop bandwidth
Example Flowgraph
This flowgraph can be found at [1].
Source Files
- C++ files
- fll_band_edge_cc_impl.cc
- Header files
- fll_band_edge_cc_impl.h
- Public header files
- fll_band_edge_cc.h
- Block definition
- digital_fll_band_edge_cc.block.yml