Quadrature Demod: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (25 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Block Docs]] | [[Category:Block Docs]] | ||
The '''Quadrature Demod''' block accepts a stream of complex samples, such as the narrow baseband stream containing the desired signal, and produces a stream of floats that represent a frequency demodulation. This block is most useful in demodulating FM, FSK, GMSK, and similar modulations that carry information through changes in frequency. | |||
delayed input and the | |||
the argument of the resulting complex number: | This block does not support C++ output, so it cannot be used when the output language of a flowgraph in GRC is C++. | ||
== Mathematical Description == | |||
The output of the block is the signal frequency in relation to the sample | |||
rate, multiplied with the gain. It produces this by calculating the product of the one-sample delayed-&-conjugated input and the undelayed signal, and then calculates the argument (a.k.a. angle, in radians) of the resulting complex number: | |||
<math>y[n] = \mathrm{arg}\left(x[n] \, \bar x [n-1]\right)</math> | <math>y[n] = \mathrm{arg}\left(x[n] \, \bar x [n-1]\right)</math> | ||
Let x be a complex sinusoid with amplitude A>0, (absolute) | Let x be a complex sinusoid with amplitude A>0, (absolute) | ||
frequency f\in\mathbb R and phase \phi_0\in[0;2\pi] sampled at | frequency <math>f\in\mathbb R</math> and phase <math>\phi_0\in[0;2\pi]</math> sampled at | ||
f_s>0 so, without loss of generality, | f_s>0 so, without loss of generality, | ||
<math>x[n]= A e^{j2\pi( \frac f{f_s} n + \phi_0)} | <math>x[n]= A e^{j2\pi( \frac f{f_s} n + \phi_0)}</math> | ||
then | then | ||
<math>y[n] = \mathrm{arg}\left(A e^{j2\pi\left( \frac f{f_s} n + \phi_0\right)} \overline{A e^{j2\pi( \frac f{f_s} (n-1) + \phi_0)}}\right)\ = \mathrm{arg}\left(A^2 e^{j2\pi\left( \frac f{f_s} n + \phi_0\right)} e^{-j2\pi( \frac f{f_s} (n-1) + \phi_0)}\right)\ = \mathrm{arg}\left( A^2 e^{j2\pi\left( \frac f{f_s} n + \phi_0 - \frac f{f_s} (n-1) - \phi_0\right)}\right)\ = \mathrm{arg}\left( A^2 e^{j2\pi\left( \frac f{f_s} n - \frac f{f_s} (n-1)\right)}\right)\ = \mathrm{arg}\left( A^2 e^{j2\pi\left( \frac f{f_s} \left(n-(n-1)\right)\right)}\right)\ | <math>y[n] = \mathrm{arg}\left(A e^{j2\pi\left( \frac f{f_s} n + \phi_0\right)} \overline{A e^{j2\pi( \frac f{f_s} (n-1) + \phi_0)}}\right)\ </math> | ||
<math> | |||
= \mathrm{arg}\left(A^2 e^{j2\pi\left( \frac f{f_s} n + \phi_0\right)} e^{-j2\pi( \frac f{f_s} (n-1) + \phi_0)}\right)\ | |||
</math> | |||
<math> | |||
= \mathrm{arg}\left( A^2 e^{j2\pi\left( \frac f{f_s} n + \phi_0 - \frac f{f_s} (n-1) - \phi_0\right)}\right)\ = \mathrm{arg}\left( A^2 e^{j2\pi\left( \frac f{f_s} n - \frac f{f_s} (n-1)\right)}\right)\ | |||
</math> | |||
<math> | |||
= \mathrm{arg}\left( A^2 e^{j2\pi\left( \frac f{f_s} \left(n-(n-1)\right)\right)}\right)\ | |||
</math> | |||
<math>A</math> is real, so is <math>A^2</math> and hence only scales, therefore <math>\mathrm{arg}(\cdot)</math> is invariant: <math> | <math> = \mathrm{arg}\left( A^2 e^{j2\pi \frac f{f_s}}\right) | ||
</math> | |||
<math>A</math> is real, and so is <math>A^2</math>, and hence only scales, therefore <math>\mathrm{arg}(\cdot)</math> is invariant: = arg <math>\left( e^{j2 \pi \frac{f}{f_s}} \right) = \frac{f}{f_s}</math> | |||
== Parameters == | == Parameters == | ||
; Gain | ; Gain | ||
: Gain setting to adjust the output amplitude. Set based on converting the phase difference between samples to a nominal output value. | : Gain setting to adjust the output amplitude. Set based on converting the phase difference between samples to a nominal output value. Default: "samp_rate/(2*math.pi*fsk_deviation_hz)". | ||
== Example Flowgraph == | == Example Flowgraph == | ||
This flowgraph shows the Quadrature Demod block as a Frequency Shift Keying detector. | === Example 1 === | ||
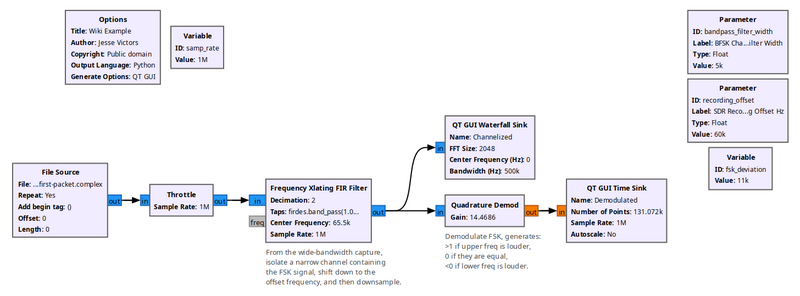
[[File:Quadrature_Demod_flowgraph.png|800px]] | |||
An example flowgraph of this block, demonstrating the demodulation of a narrow FSK signal inside a wideband capture file. | |||
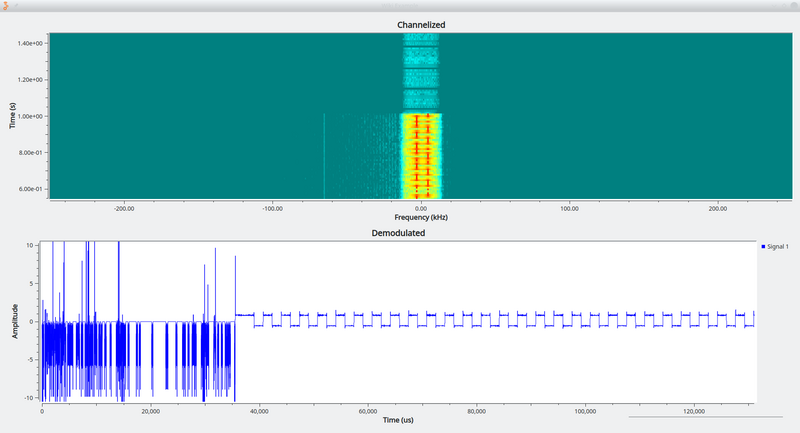
[[File:Quadrature_Demod_example.png|800px]] | |||
The Quadrature Demod block in practice extracts the symbols from the FSK signal. Random noise is produced before and after the signal. | |||
This flowgraph shows the Quadrature Demod block as a Frequency Shift Keying detector. First, the [[Frequency Xlating FIR Filter]] acts as a channelizer, extracting a narrow baseband signal from a wider stream. Then the Quadrature Demod block returns floats that are >1 if the upper frequency is louder, 0 if they are equal, and <0 if the lower frequency is louder, thus demodulating FSK. In this scenario, if <code>fsk_deviation</code> is defined as the difference between the upper and lower frequencies, and the baseband sampling rate is known (after the decimating from the Freq Xlating FIR Filter block), then a good formula for the Gain parameter would be <code>baseband_samp_rate / (math.pi * fsk_deviation)</code>. This causes the block to produce output floats that will never have a magnitude greater than 1.0 for the actual symbols. | |||
=== Example 2 === | |||
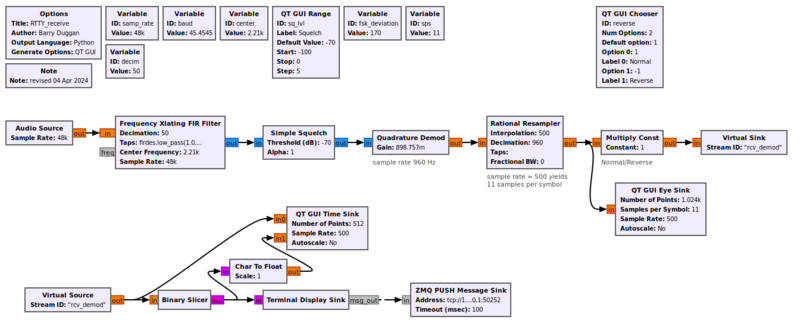
[[File:RTTY_rcv.png|800px]] | [[File:RTTY_rcv.png|800px]] | ||
This flowgraph shows BFSK signal recovery using Quadrature Demod block | |||
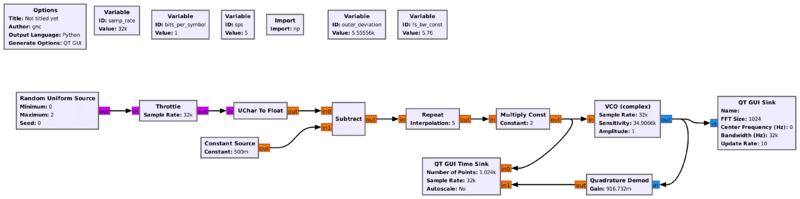
[[File:FSK2_mod_demod.png|800px]] | |||
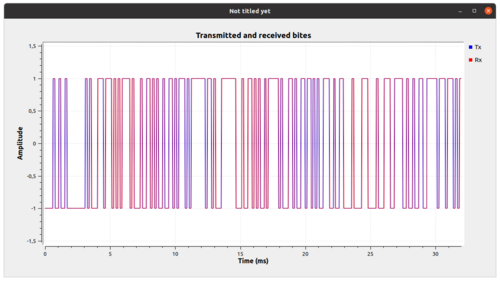
Transmitted and received bits using above example | |||
[[File:BFSK_tx_rx.png|500px]] | |||
== Source Files == | == Source Files == | ||
; C++ files | ; C++ files | ||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/master/gr-analog/lib/quadrature_demod_cf_impl.cc] | : [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/master/gr-analog/lib/quadrature_demod_cf_impl.cc quadrature_demod_cf_impl.cc] | ||
; Header files | ; Header files | ||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/master/gr-analog/lib/quadrature_demod_cf_impl.h] | : [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/master/gr-analog/lib/quadrature_demod_cf_impl.h quadrature_demod_cf_impl.h] | ||
; Public header files | ; Public header files | ||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/master/gr-analog/include/gnuradio/analog/quadrature_demod_cf.h] | : [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/master/gr-analog/include/gnuradio/analog/quadrature_demod_cf.h quadrature_demod_cf.h] | ||
; Block definition | ; Block definition | ||
: [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/master/gr-analog/grc/analog_quadrature_demod_cf.block.yml] | : [https://github.com/gnuradio/gnuradio/blob/master/gr-analog/grc/analog_quadrature_demod_cf.block.yml analog_quadrature_demod_cf.block.yml] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:56, 18 April 2023
The Quadrature Demod block accepts a stream of complex samples, such as the narrow baseband stream containing the desired signal, and produces a stream of floats that represent a frequency demodulation. This block is most useful in demodulating FM, FSK, GMSK, and similar modulations that carry information through changes in frequency.
This block does not support C++ output, so it cannot be used when the output language of a flowgraph in GRC is C++.
Mathematical Description
The output of the block is the signal frequency in relation to the sample rate, multiplied with the gain. It produces this by calculating the product of the one-sample delayed-&-conjugated input and the undelayed signal, and then calculates the argument (a.k.a. angle, in radians) of the resulting complex number:
Let x be a complex sinusoid with amplitude A>0, (absolute) frequency and phase sampled at f_s>0 so, without loss of generality,
then
is real, and so is , and hence only scales, therefore is invariant: = arg
Parameters
- Gain
- Gain setting to adjust the output amplitude. Set based on converting the phase difference between samples to a nominal output value. Default: "samp_rate/(2*math.pi*fsk_deviation_hz)".
Example Flowgraph
Example 1
An example flowgraph of this block, demonstrating the demodulation of a narrow FSK signal inside a wideband capture file.
The Quadrature Demod block in practice extracts the symbols from the FSK signal. Random noise is produced before and after the signal.
This flowgraph shows the Quadrature Demod block as a Frequency Shift Keying detector. First, the Frequency Xlating FIR Filter acts as a channelizer, extracting a narrow baseband signal from a wider stream. Then the Quadrature Demod block returns floats that are >1 if the upper frequency is louder, 0 if they are equal, and <0 if the lower frequency is louder, thus demodulating FSK. In this scenario, if fsk_deviation is defined as the difference between the upper and lower frequencies, and the baseband sampling rate is known (after the decimating from the Freq Xlating FIR Filter block), then a good formula for the Gain parameter would be baseband_samp_rate / (math.pi * fsk_deviation). This causes the block to produce output floats that will never have a magnitude greater than 1.0 for the actual symbols.
Example 2
This flowgraph shows BFSK signal recovery using Quadrature Demod block
Transmitted and received bits using above example
Source Files
- C++ files
- quadrature_demod_cf_impl.cc
- Header files
- quadrature_demod_cf_impl.h
- Public header files
- quadrature_demod_cf.h
- Block definition
- analog_quadrature_demod_cf.block.yml
![{\displaystyle y[n]=\mathrm {arg} \left(x[n]\,{\bar {x}}[n-1]\right)}](https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/84c630130d2bec382313f6da607e7df434cc7613)

![{\displaystyle \phi _{0}\in [0;2\pi ]}](https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/83317d39f55e8bd895248ce082aa5b5dac28adb5)
![{\displaystyle x[n]=Ae^{j2\pi ({\frac {f}{f_{s}}}n+\phi _{0})}}](https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7480ee4b1d7e60697cc5c58bd0e033bcb0be868b)
![{\displaystyle y[n]=\mathrm {arg} \left(Ae^{j2\pi \left({\frac {f}{f_{s}}}n+\phi _{0}\right)}{\overline {Ae^{j2\pi ({\frac {f}{f_{s}}}(n-1)+\phi _{0})}}}\right)\ }](https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2832f97c99af7f007a0e341db9a884aa61ad9594)