Quadrature Demod: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
Mathematically, this block calculates the product of the one-sample | Mathematically, this block calculates the product of the one-sample | ||
delayed input and the conjugate undelayed signal, and then calculates | delayed input and the conjugate undelayed signal, and then calculates | ||
the argument of the resulting complex number: | the argument (a.k.a. angle, in radians) of the resulting complex number: | ||
<math>y[n] = \mathrm{arg}\left(x[n] \, \bar x [n-1]\right)</math> | <math>y[n] = \mathrm{arg}\left(x[n] \, \bar x [n-1]\right)</math> | ||
Revision as of 07:05, 4 December 2020
This can be used to demod FM, FSK, GMSK, etc. The input is complex baseband, output is the signal frequency in relation to the sample rate, multiplied with the gain.
Mathematically, this block calculates the product of the one-sample delayed input and the conjugate undelayed signal, and then calculates the argument (a.k.a. angle, in radians) of the resulting complex number:
Let x be a complex sinusoid with amplitude A>0, (absolute) frequency f\in\mathbb R and phase sampled at f_s>0 so, without loss of generality,
then
is real, so is and hence only scales, therefore is invariant: = arg
Parameters
- Gain
- Gain setting to adjust the output amplitude. Set based on converting the phase difference between samples to a nominal output value.
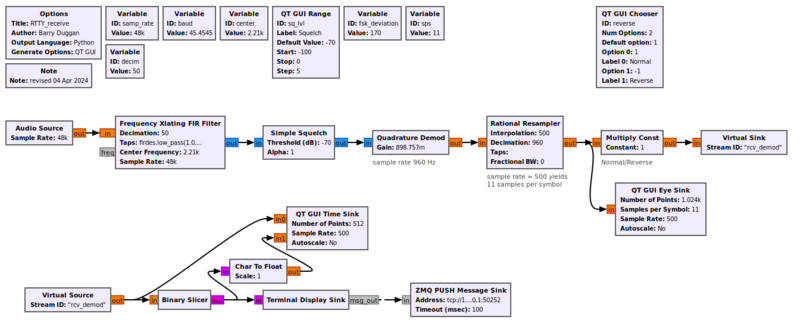
Example Flowgraph
This flowgraph shows the Quadrature Demod block as a Frequency Shift Keying detector.
Source Files
- C++ files
- [1]
- Header files
- [2]
- Public header files
- [3]
- Block definition
- [4]
![{\displaystyle y[n]=\mathrm {arg} \left(x[n]\,{\bar {x}}[n-1]\right)}](https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/84c630130d2bec382313f6da607e7df434cc7613)
![{\displaystyle \phi _{0}\in [0;2\pi ]}](https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/83317d39f55e8bd895248ce082aa5b5dac28adb5)
![{\displaystyle x[n]=Ae^{j2\pi ({\frac {f}{f_{s}}}n+\phi _{0})}\ f}](https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c7a69a54378a39cf1805ca54252709cb29b017ff)
![{\displaystyle y[n]=\mathrm {arg} \left(Ae^{j2\pi \left({\frac {f}{f_{s}}}n+\phi _{0}\right)}{\overline {Ae^{j2\pi ({\frac {f}{f_{s}}}(n-1)+\phi _{0})}}}\right)\ =\mathrm {arg} \left(A^{2}e^{j2\pi \left({\frac {f}{f_{s}}}n+\phi _{0}\right)}e^{-j2\pi ({\frac {f}{f_{s}}}(n-1)+\phi _{0})}\right)\ =\mathrm {arg} \left(A^{2}e^{j2\pi \left({\frac {f}{f_{s}}}n+\phi _{0}-{\frac {f}{f_{s}}}(n-1)-\phi _{0}\right)}\right)\ =\mathrm {arg} \left(A^{2}e^{j2\pi \left({\frac {f}{f_{s}}}n-{\frac {f}{f_{s}}}(n-1)\right)}\right)\ =\mathrm {arg} \left(A^{2}e^{j2\pi \left({\frac {f}{f_{s}}}\left(n-(n-1)\right)\right)}\right)\ =\mathrm {arg} \left(A^{2}e^{j2\pi {\frac {f}{f_{s}}}}\right)}](https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/cd12a233f670bb1276175b55b2fed0d7394085ba)