Hier Blocks and Parameters: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Mattcarrick (talk | contribs) |
Mattcarrick (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
[[File:StartingFlowgraphHierBlock.png|700px]] | [[File:StartingFlowgraphHierBlock.png|700px]] | ||
Update the ''QT GUI Range'' properties: | |||
* Id: ''frequency'' | |||
* Default Value: ''0'' | |||
* Start: ''-samp_rate/2'' | |||
* Stop: ''samp_rate/2'' | |||
Revision as of 17:09, 12 January 2022
This tutorial describes how to create a hierarchical block, or Hier block, in GRC. The previous tutorial, Creating Your First Block, demonstrates how to create your first GNU Radio block using the Embedded Python Block.
Creating a Flowgraph
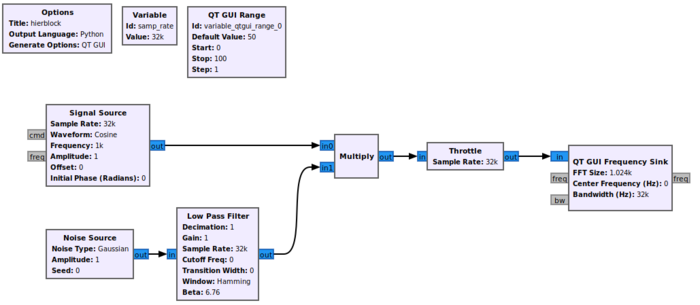
A hier block is used to encapsulate and simplify multiple GNU Radio blocks into a single block. The example hier block will be a frequency shifter block which multiplies a Signal Source against an input signal.
The first step is creating the flowgraph. Drag and drop the following blocks into the workspace:
- Signal Source
- Multiply
- Noise Source
- Low Pass Filter
- Throttle
- QT GUI Frequency Sink
- QT GUI Range
Connect the blocks:
Update the QT GUI Range properties:
- Id: frequency
- Default Value: 0
- Start: -samp_rate/2
- Stop: samp_rate/2