Hier Blocks and Parameters: Difference between revisions
Mattcarrick (talk | contribs) |
Mattcarrick (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
[[File:OptionsSelectHierBlock.png|500px]] | [[File:OptionsSelectHierBlock.png|500px]] | ||
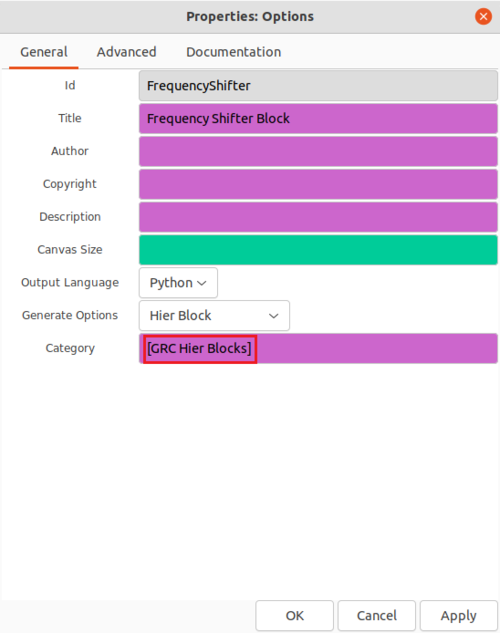
The remaining properties will then change, showing the ''Category'': | |||
[[File:ShowGRCHierBlocksCategory.png|500px]] | |||
Revision as of 17:33, 12 January 2022
This tutorial describes how to create a hierarchical block, or Hier block, in GRC. The previous tutorial, Creating Your First Block, demonstrates how to create your first GNU Radio block using the Embedded Python Block.
Creating the Flowgraph
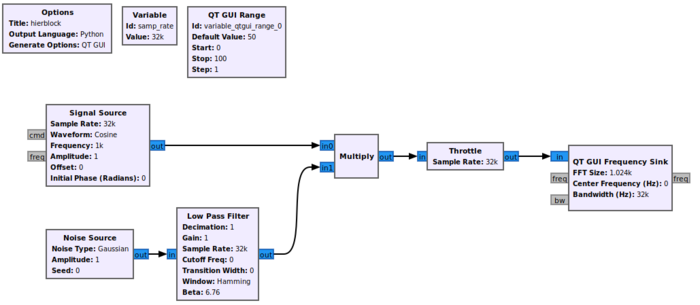
A hier block is used to encapsulate and simplify multiple GNU Radio blocks into a single block. The example hier block will be a frequency shifter block which multiplies a Signal Source against an input signal.
The first step is creating the flowgraph. Drag and drop the following blocks into the workspace:
- Signal Source
- Multiply
- Noise Source
- Low Pass Filter
- Throttle
- QT GUI Frequency Sink
- QT GUI Range
Connect the blocks:
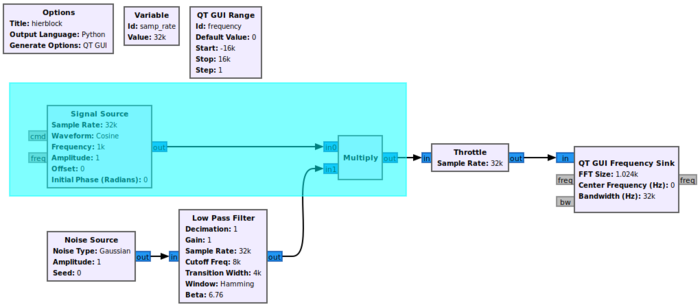
Update the QT GUI Range properties:
- Id: frequency
- Default Value: 0
- Start: -samp_rate/2
- Stop: samp_rate/2
Update the Low Pass Filter properties:
- Cutoff Freq (Hz): samp_rate/4
- Transition Width (Hz): samp_rate/8
Create The Hier Block
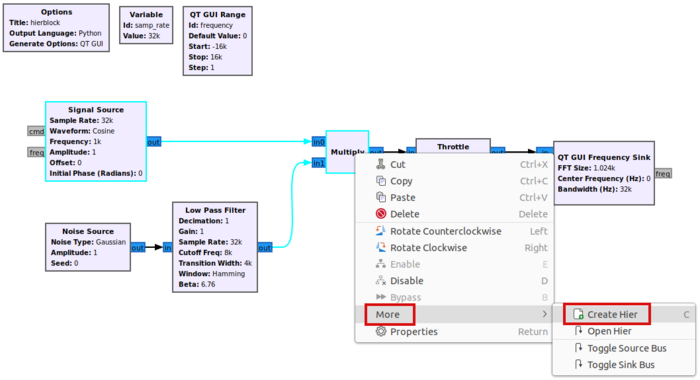
Click and drag in the workspace window to select the Signal Source and Multiply blocks, as well as the connection between them:
Right-click on the highlighted blocks and select More > Create Hier:
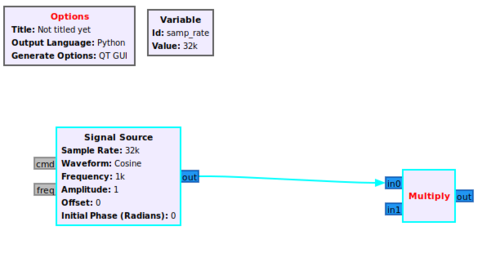
A flowgraph will be created in a new GRC tab:
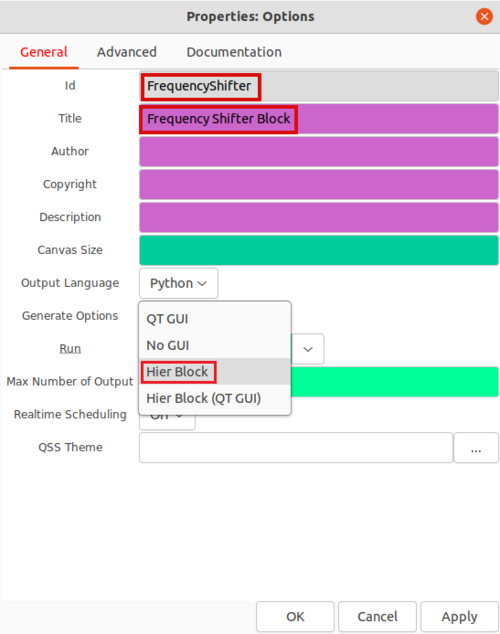
Double-click the Options block and edit the properties. Update the properties:
- Id: FrequencyShifter
- Title: Frequency Shifter Block
- Generate Options: Hier Block
The remaining properties will then change, showing the Category: