Constellation Rect. Object: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
== Example Flowgraph == | == Example Flowgraph == | ||
This flowgraph is taken from the [[ | This flowgraph is taken from the [[QPSK_Mod_and_Demod]] tutorial. | ||
[[File: | [[File:Qpsk_stage1_fg.png|800px]] | ||
== Source Files == | == Source Files == | ||
Latest revision as of 14:59, 9 December 2023
A version of Constellation Object specific to rectangular constellations. See Constellation Object for more usage info.
Parameters
- Symbol Map
- List of alphabet symbols (before applying any differential coding) (order of list matches Constellation Points)
- Constellation Points
- List of constellation points (order of list matches Symbol Map)
- Rotational Symmetry
- Number of rotations around unit circle that have the same representation.
- Real Sectors
- Number of sectors the real axis is split in to.
- Imaginary Sectors
- Number of sectors the imag axis is split in to.
- Width Real Sectors
- Width of each real sector to calculate decision boundaries.
- Width Imaginary Sectors
- Width of each imag sector to calculate decision boundaries.
- Soft Bits Precision
- The number of bits of precision used when generating the LUT.
- Soft Decisions LUT
- The soft decision LUT as a vector of tuples (vectors in C++) of soft decisions. Each element of the LUT is a vector of k-bit floats (where there are k bits/sample in the constellation).
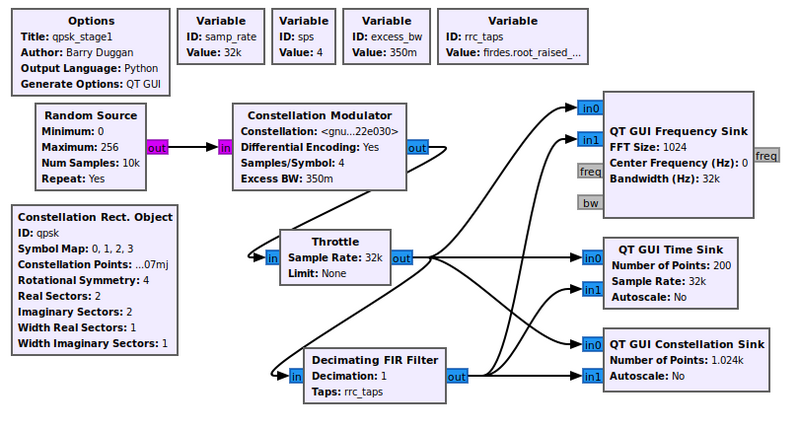
Example Flowgraph
This flowgraph is taken from the QPSK_Mod_and_Demod tutorial.
Source Files
- C++ files
- constellation.cc
- Header files
- TODO
- Public header files
- constellation.h
- Block definition
- digital_constellation_rect.block.yml