Talk:ModuleNotFoundError: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
IndianaM1ke (talk | contribs) (Tweak variable substitution to CAPS and fix Python directory to be full MAJOR.MINOR) |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
If you don't know or remember your installation prefix, perform the following step: | If you don't know or remember your installation prefix, perform the following step: | ||
* on a terminal screen, enter <code>gnuradio-config-info --prefix</code> | * on a terminal screen, enter <code>gnuradio-config-info --prefix</code> | ||
then use that prefix in place of <code>{ | then use that prefix in place of <code>{PREFIX}</code> in the following commands. | ||
== C. Finding the Python library == | == C. Finding the Python library == | ||
Using your file manager, look in <code>{ | Using your file manager, look in <code>{PREFIX}/lib</code> for a directory to match your Python version. For example, <code>python2.7</code> or <code>python3.7</code>; note the combination of <code>python</code> and the version as <code>{major}.{minor}</code>, which is used by all Python installs by default. Use that directory name in place of <code>{PY-VERSION}</code> in the following commands. | ||
== D. Setting PYTHONPATH == | == D. Setting PYTHONPATH == | ||
| Line 30: | Line 29: | ||
- For almost all Debian / Ubuntu (and derivative) systems, and most other 32-bit Unix/Linux systems, use: | - For almost all Debian / Ubuntu (and derivative) systems, and most other 32-bit Unix/Linux systems, use: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
export PYTHONPATH={ | export PYTHONPATH={PREFIX}/lib/{PY-VERSION}/dist-packages:{PREFIX}/lib/{PY-VERSION}/site-packages:$PYTHONPATH | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
- For other 64-bit systems, use: | - For other 64-bit systems, use: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
export PYTHONPATH={ | export PYTHONPATH={PREFIX}/lib64/{PY-VERSION}/site-packages:$PYTHONPATH | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| Line 42: | Line 41: | ||
- For almost all Debian / Ubuntu (and derivative) systems, and most other 32-bit Unix/Linux systems, use: | - For almost all Debian / Ubuntu (and derivative) systems, and most other 32-bit Unix/Linux systems, use: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH={ | export LD_LIBRARY_PATH={PREFIX}/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
- For other 64-bit systems, use: | - For other 64-bit systems, use: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH={ | export LD_LIBRARY_PATH={PREFIX}/lib64:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Revision as of 14:11, 30 January 2020
When you start gnuradio-companion or execute grcc, and you get this, or a similar, error message:
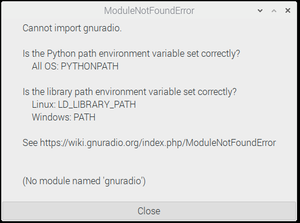
then perform the following steps.
A. Mac OSX / macOS
See the MacInstall guide for issues and settings for that OS.
B. Determine your installation prefix
If you don't know or remember your installation prefix, perform the following step:
- on a terminal screen, enter
gnuradio-config-info --prefix
then use that prefix in place of {PREFIX} in the following commands.
C. Finding the Python library
Using your file manager, look in {PREFIX}/lib for a directory to match your Python version. For example, python2.7 or python3.7; note the combination of python and the version as {major}.{minor}, which is used by all Python installs by default. Use that directory name in place of {PY-VERSION} in the following commands.
D. Setting PYTHONPATH
- For almost all Debian / Ubuntu (and derivative) systems, and most other 32-bit Unix/Linux systems, use:
export PYTHONPATH={PREFIX}/lib/{PY-VERSION}/dist-packages:{PREFIX}/lib/{PY-VERSION}/site-packages:$PYTHONPATH
- For other 64-bit systems, use:
export PYTHONPATH={PREFIX}/lib64/{PY-VERSION}/site-packages:$PYTHONPATH
E. Setting LD_LIBRARY_PATH
- For almost all Debian / Ubuntu (and derivative) systems, and most other 32-bit Unix/Linux systems, use:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH={PREFIX}/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
- For other 64-bit systems, use:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH={PREFIX}/lib64:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
F. Store the commands in a Bash start-up file
Once you have determined the correct two export commands to use, open your text editor and put them in your ~/.profile or ~/.bash_aliases or ~/.bashrc file and restart your terminal.