Audio Sink: Difference between revisions
(add Windows to Device Name) |
(remove ref to ALSAPulseAudio; use better example) |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
On Linux, typical choices include: | On Linux, typical choices include: | ||
* hw:0,0 | * hw:0,0 | ||
* plughw:0,0 | * plughw:0,0 | ||
* pulse | |||
For ALSA users with audio trouble, follow this procedure: | For ALSA users with audio trouble, follow this procedure: | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
* find the entry such as: | * find the entry such as: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
hw:CARD=Generic,DEV=0 | |||
HD-Audio Generic, ALC662 rev3 Analog | |||
Direct hardware device without any conversions | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
from the list which matches your device. | from the list which matches your device. If you have an HDMI monitor, find an appropriate entry with "HDMI". | ||
* use the first line of that entry (e.g. "hw:CARD= | * use the first line of that entry (e.g. "hw:CARD=Generic,DEV=0") as the device name (without the quotes). | ||
==== Windows ==== | ==== Windows ==== | ||
Revision as of 12:40, 4 July 2020
Allows a signal to be played through your speakers or other audio device
Parameters
Sample Rate
To set the Audio sampling rate, click the drop-down menu to see popular rates. Note: not all sampling rates will be supported by your hardware. For typical applications, this should be set to 48kHz.
Device Name
Leave the device name blank to choose the default audio device. Selecting a specific device name depends on the OS.
OSX
On OSX, go into the System Preferences, click on "Sound", and then the "Output" tab. The listings under "Name" contain the exact device names currently available; if a new audio sink is attached to the computer then a new name will appear -- for example "Headphones" for some Macs. Since most such device names contain spaces, make sure to put quotes around the name argument, for example:
spectrum_inversion.py -O "MacBook Pro Speakers"
Linux
On Linux, typical choices include:
- hw:0,0
- plughw:0,0
- pulse
For ALSA users with audio trouble, follow this procedure:
- from a terminal window enter:
aplay -L
- find the entry such as:
hw:CARD=Generic,DEV=0
HD-Audio Generic, ALC662 rev3 Analog
Direct hardware device without any conversions
from the list which matches your device. If you have an HDMI monitor, find an appropriate entry with "HDMI".
- use the first line of that entry (e.g. "hw:CARD=Generic,DEV=0") as the device name (without the quotes).
Windows
On Windows, go into the Settings, cllck on "System", click on "Sound", and then the "Output" tab. The listings under "Name" contain the exact device names currently available; if a new audio sink is attached to the computer then a new name will appear, for example "Headphones". Since most of the device names contain spaces, make sure to put quotes around the name argument, for example:
"Speakers (Realtek High Definition Audio)"
OK to Block
On by default, which should be used when this sink is not throttled by any other block.
Num Inputs
The audio sink can have multiple inputs depending upon your hardware. For example, set the inputs to 2 for stereo or 1 for mono.
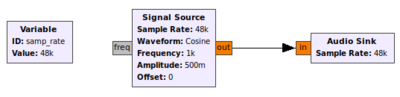
Example Flowgraph
This flowgraph should play a 1 kHz tone out of your speakers. Note that you don't need a throttle block, the Audio Sink should throttle for you. If you do end up using an already-throttled signal source, then set "OK to Block" to No.