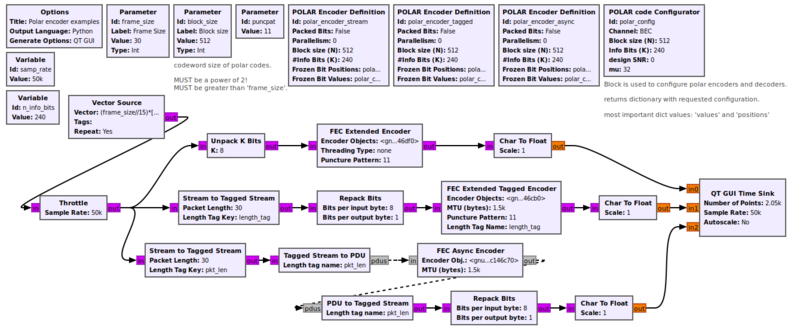
POLAR Encoder Definition
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
POLAR encoder
Polar codes are based on this paper by Erdal Arikan "Channel Polarization: A Method for Constructing Capacity-Achieving Codes for Symmetric Binary-Input Memoryless Channels", 2009 block holds common information for encoders and decoders.
Expects values with MSB first. It needs a full information word and encodes it in one pass. Output is a codeword of block_size.
Parameters
- Packed Bits
- Choose 1 active bit per byte or 8 active bit per byte. if false, VOLK polar encoder is used.
- Parallelism
- For parallel execution of multiple instances of the block (more info is needed on this)
- Dimension 1
- For parallelism
- Dimension 2
- For parallelism
- Block size (N)
- Codeword size. MUST be a power of 2.
- #Info Bits (K)
- Represents the number of information bits in a block. Also called frame_size. <= block_size
- Frozen Bit Positions
- Integer vector which defines the position of all frozen bits in a block. Its size MUST be equal to block_size - num_info_bits. Also it must be sorted and every position must only occur once.
- Frozen Bit Values
- Holds an unpacked byte for every frozen bit position. It defines if a frozen bit is fixed to '0' or '1'. Defaults to all ZERO.
Example Flowgraph
This flowgraph can be found at [1]
Source Files
- C++ files
- [2]
- Common code
- Public header files
- [3]
- Block definition
- [4]