Streams and Vectors: Difference between revisions
Mattcarrick (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Mattcarrick (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Streams == | == Streams == | ||
''Streams'' in GNU Radio are what convey the information between blocks | ''Streams'' in GNU Radio are what convey the information between blocks and are represented by the arrows connecting blocks in a flowgraph. A ''stream'' must have a data type, such as ''Float 32'' or ''Byte''. A ''stream'' carries 1 sample for each time instance and are used to represent and process serial data. | ||
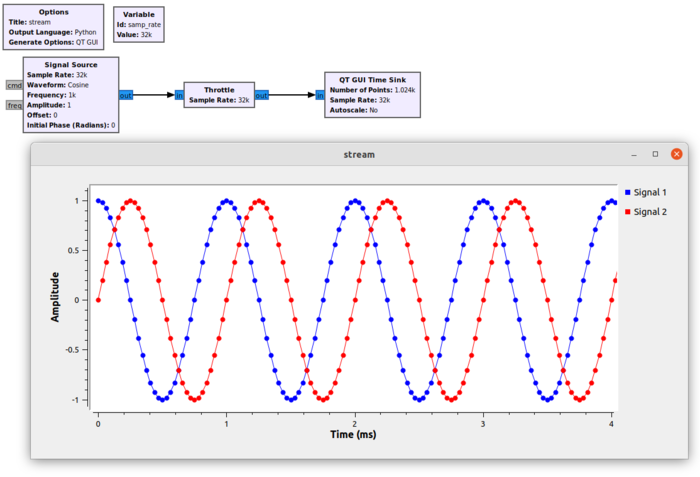
The ''Signal Source'' block produces a ''Complex Float 32'' stream. The output of the block at each time instance contains 1 complex sample: | |||
[[File:SignalSourceStreamExample.png|700px]] | |||
Revision as of 17:42, 6 January 2022
This tutorial will describe the difference between a Stream and a Vector. You can find the previous tutorial here: Converting Data Types
Streams
Streams in GNU Radio are what convey the information between blocks and are represented by the arrows connecting blocks in a flowgraph. A stream must have a data type, such as Float 32 or Byte. A stream carries 1 sample for each time instance and are used to represent and process serial data.
The Signal Source block produces a Complex Float 32 stream. The output of the block at each time instance contains 1 complex sample:
- note: use an image
each time instance carries 1 sample
Vectors
Where streams carry 1 sample per time instance, vectors can carry multiple samples per time instance. By analogy, a stream represents a scalar at each time instance, whereas a vector represents an array at each time instance. Vectors allow data to be represent and process data in parallel.
darker color in GRC
- note: use an image