VCO (complex): Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (remove extraneous link) |
(add example flowgraph) |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
== Example Flowgraph == | == Example Flowgraph == | ||
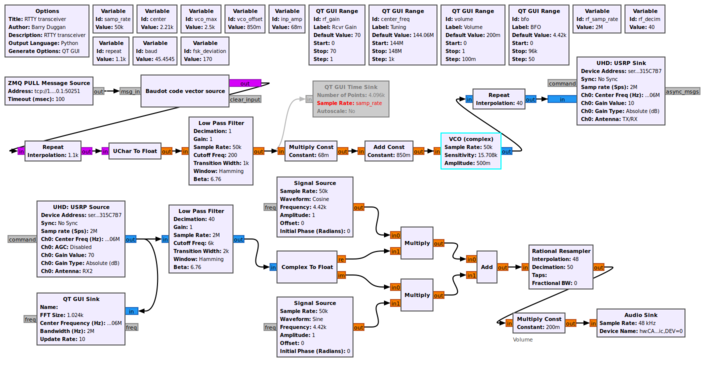
This flowgraph shows a Radioteletype (RTTY) transmitter and receiver. The upper portion is the transmitter. The parameters for the VCO are explained in [[VCO]].<br> | |||
The lower portion of the flowgraph is a single sideband (SSB) receiver. The audio can be fed into a RTTY decoder such as shown in [[Sample_Rate_Tutorial#Source_hardware_example]]. | |||
[[File:USRP_RTTY_fg.png|710px]] | |||
== Source Files == | == Source Files == | ||
Revision as of 19:35, 27 July 2020
VCO - Voltage controlled oscillator. Produces a sinusoid of frequency based on the amplitude of the input. See VCO for a real (not complex) sinusoidal output.
input: float stream of control voltages;
output: complex oscillator output
Parameters
- Sample Rate
- sampling rate (Hz)
- Sensitivity
- units are radians/sec/volt
- Amplitude
- output amplitude
Example Flowgraph
This flowgraph shows a Radioteletype (RTTY) transmitter and receiver. The upper portion is the transmitter. The parameters for the VCO are explained in VCO.
The lower portion of the flowgraph is a single sideband (SSB) receiver. The audio can be fed into a RTTY decoder such as shown in Sample_Rate_Tutorial#Source_hardware_example.
Source Files
- C++ files
- TODO
- Header files
- TODO
- Public header files
- TODO
- Block definition
- TODO