Low Pass Filter Example
| Beginner Tutorials
Introducing GNU Radio Flowgraph Fundamentals
Creating and Modifying Python Blocks DSP Blocks
SDR Hardware |
This tutorial describes how to use a low-pass filter in GNU Radio.
The previous tutorial, Python Block Tags, describes how to read and write tags in a Python block. The next tutorial, Designing Filter Taps, describes how to design a set of low-pass filter taps and apply them against a signal.
Creating the Flowgraph
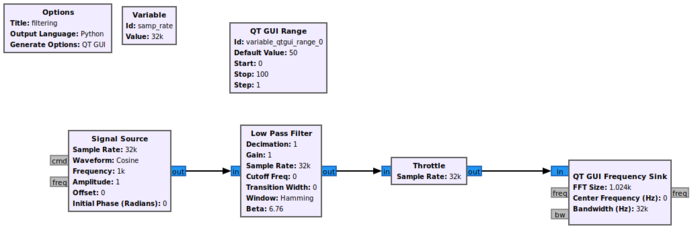
Begin by adding the following blocks to the GRC work space:
- Signal Source
- Low Pass Filter
- Throttle
- QT GUI Frequency Sink
- QT GUI Range
Connect the blocks in the following manner:
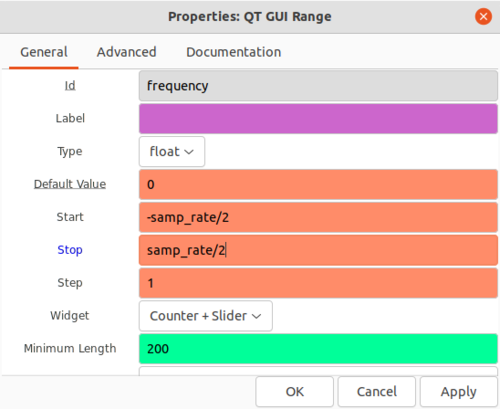
The QT GUI Range block is used to control the frequency of the Signal Source block. Double-click the QT GUI Range block and edit the properties:
- Id: frequency
- Default Value: 0
- Start: -samp_rate/2
- Stop: samp_rate/2
Click OK to save.
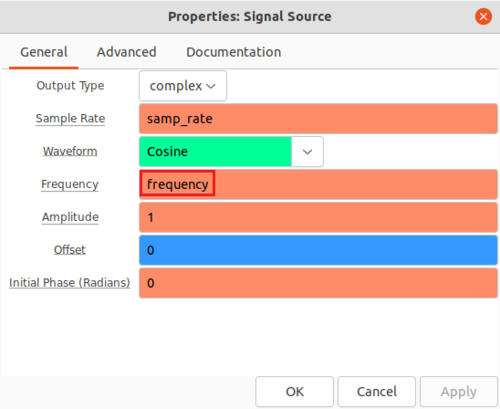
Double-click the Signal Source block and enter frequency from the QT GUI Range variable:
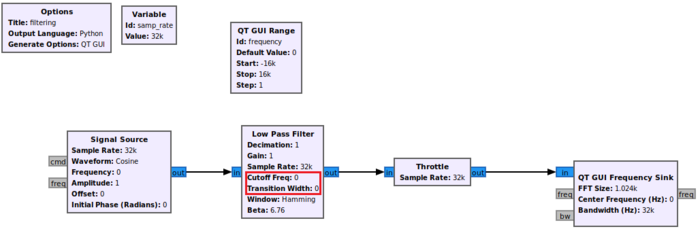
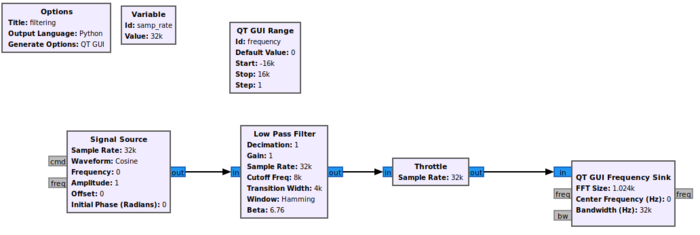
Click OK to save. The flowgraph looks like the following image. Notice that the Low Pass Filter has a Cutoff Freq and Transition Width of 0:
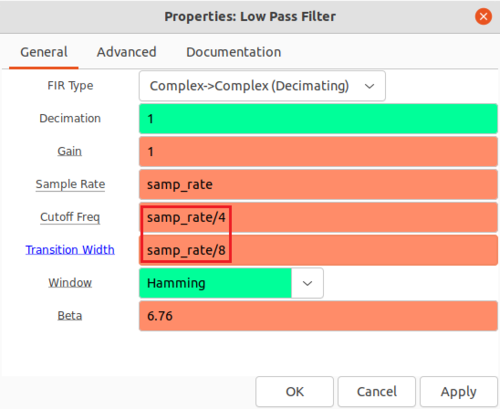
Double-click the Low Pass Filter block and edit the properties:
- Cutoff freq: samp_rate/4
- Transition Width: samp_rate/8
The flowgraph is complete and looks like the following:
Run the Flowgraph
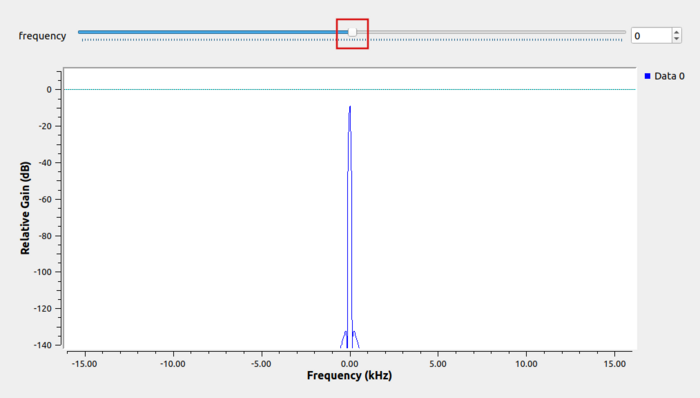
The flowgraph is complete! Run the flowgraph. The QT GUI Frequency Sink appears with a frequency slider bar:
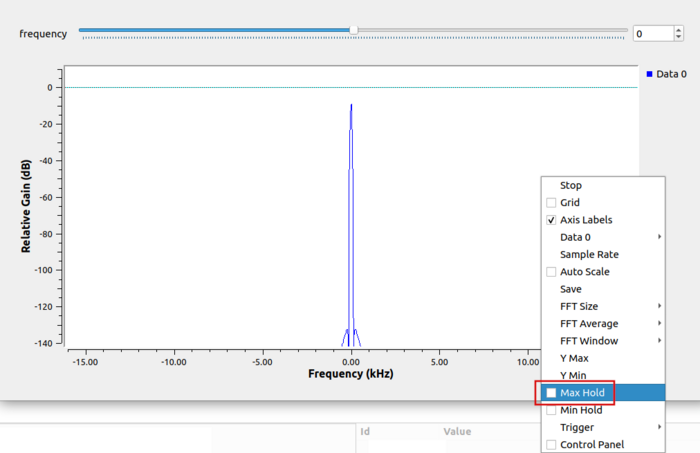
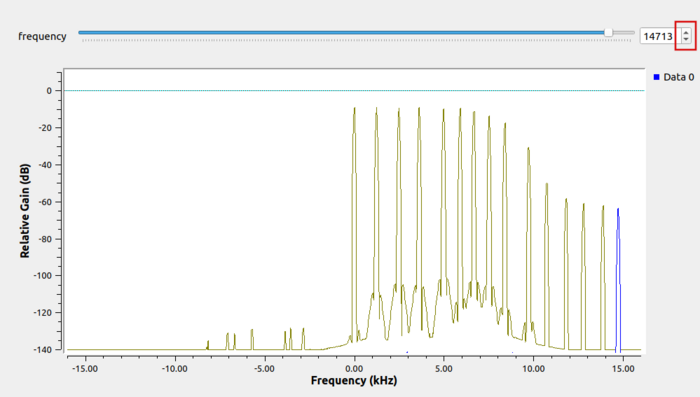
Scroll-wheel-click on the QT GUI Frequency window and select Max Hold:
The Max Hold option retains and displays the maximum value at each frequency until the the flowgraph is closed. Clicking through multiple values of the frequency slider bar at the top shows the low pass filter response:
Noise Instead of Signal
Lastly, try replacing the Signal Noise with a Noise Source (or Fast Noise Source, they do the same thing), and note how the output changes.
Next Steps
The next tutorial, Designing Filter Taps, describes how to design a set of low-pass filter taps and apply them against a signal.